The objective of radiation therapy is to kill uterine cancer cells for a maximum probability of cure or palliation with a minimum of side effects. Radiation therapy is occasionally given before surgery to shrink the tumor.
![[PDF] The role of interstitial brachytherapy in the](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/f61a53da0bbcb698209c7013596f9d5e7cfeadfb/3-Figure1-1.png)
But, to fully capitalize on their value, these tools must be placed in the hands of professionals who.
Radiation therapy for uterine cancer. Radiation treatment options for uterine cancer. Radiation therapy may cause or increase vaginal discharge. This is called adjuvant therapy.
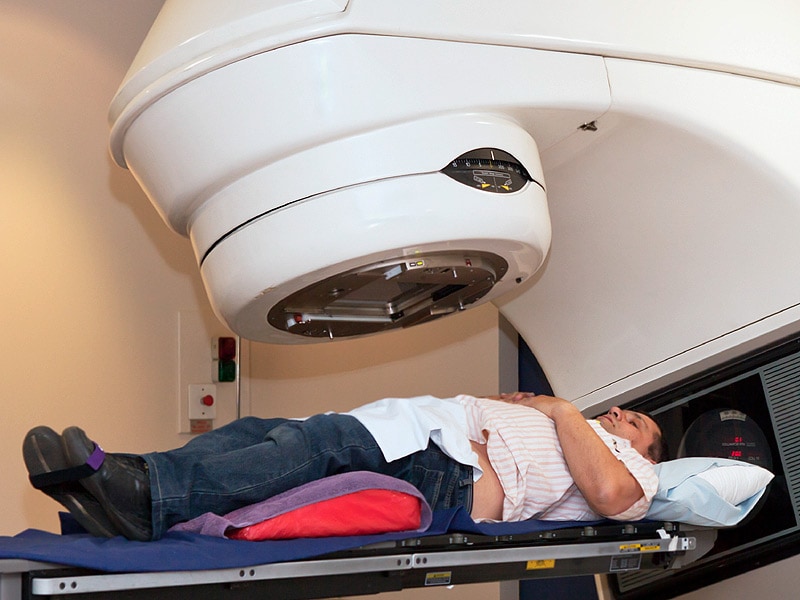
It treats the upper part of the vagina that was near the uterus. Internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. External beam radiation therapy (ebrt):
Radiation therapy can be used to prevent local cancer recurrences after surgery (adjuvant therapy) or for the treatment of recurrent cancer. It can be given in 2 ways to treat endometrial cancer: This is the most common form of radiation treatment.
For uterine cancer treatment we provide two types of radiation therapy: How much the cancer has spread (the stage). The national cancer database was used to identify women with stage iii endometrioid, serous, and clear cell uterine cancer treated with either chemotherapy (with or without vaginal brachytherapy) alone, external beam radiation (with or without brachytherapy), or combination chemotherapy and external beam radiation (with or without vaginal brachytherapy) from 2004.
Hormones are substances that control some body functions, including the. By putting radioactive materials inside the body. Endometrial cancer is a common female malignancy.
Learn more on radiation therapy for uterine cancer. Intensity modulated radiation therapy (imrt) is a radiation technique which is currently being investigated for treatment of gynecologic malignancies including endometrial cancer. In some cases, radiation therapy may be recommended as the main treatment if other health conditions mean you are not well enough for a major operation.
Rt was delivered to symptomatic lesions (both the primary mass and/or metastatic regional lymph nodes). Radiation therapy can be used to prevent local cancer recurrences after surgery (adjuvant therapy) or for the treatment of recurrent cancer. The incidence of tumor involvement of the lus was 19%;
Do not wash with douches as this may cause infection. Radiation therapy for uterine cancer. Ebrt delivers radiation to the uterine cancer cells from outside the body using a machine called a linear accelerator to direct high.
The effectiveness of radiation therapy for uterine cancer is truly set apart by expert radiation oncologists. This is called internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy. It is usually used to treat uterine cancer.
And of the corpus, 67%. A comparative analysis of the therapeutic results and causes of failure after treatment by radiation combined with surgery or radiation therapy alone eur j gynaecol oncol , 9 ( 1988 ) , pp. Postoperative radiation therapy was administered for adverse histologic criteria, including deep myometrial invasion, high grade, or lus involvement.
Some women with uterine cancer need surgery (see above) and radiation therapy. Radiation therapy is occasionally given before surgery to shrink the tumor. Radiation therapy for uterine cancer.
Radiation therapy for uterine cancer. But, to fully capitalize on their value, these tools must be placed in the hands of professionals who. Some people need both an external radiation treatment (often for a few minutes each day for 4 to 5 weeks) followed by internal radiation (often 2 to 3 sessions).
The objective of radiation therapy is to kill uterine cancer cells for a maximum probability of cure or palliation with a minimum of side effects. Hormonal therapy for uterine cancer. Your healthcare team will consider your personal needs to plan the type and amount of radiation, and when and how it is given.
Despite complete resection, patients with stage iii or iv are at high risk of local or distant recurrence. Two types of radiation treatments may used for uterine sarcoma: It is a treatment that adds, blocks or removes hormones.
Radiation therapy, also called radiotherapy, is an important part of the treatment plan for many patients with uterine cancer. At moffitt cancer center, our patients have access to the latest innovations in radiation treatment equipment and machinery. The purpose of this study is to assess the risk of uterine malignancy in patients previously treated for cervical cancer with radiation therapy.
We may advise that radiation be applied externally or internally — or both — through one of the following approaches. Which method is used depends on: The objective of radiation therapy is to kill uterine cancer cells for a maximum probability of cure or palliation with a minimum of side effects.
Let your treatment team know if the discharge smells bad or has blood in it. Sometimes both brachytherapy and external beam radiation therapy are used. For cancer of the uterus, radiation therapy is commonly used as an additional treatment after surgery to reduce the chance of the disease coming back.
Systemic adjuvant treatment includes chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Radiation therapy can be used to prevent local cancer recurrences after surgery (adjuvant therapy) or for the treatment of recurrent cancer. You may also receive other treatments.
Radiation therapy can be used to prevent local cancer recurrences after surgery (adjuvant therapy) or for the treatment of. The objective of radiation therapy is to kill uterine cancer cells for a maximum probability of cure or palliation with a minimum of side effects. Skin redness, soreness and swelling.
How much of the pelvis needs to be exposed to radiation therapy and the type (s) of radiation used depend on the extent of the disease. The radiation therapy is most often given after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. This technique allows for decreased radiation doses to critical structures such as bone marrow or small bowel while continuing to treat the tumor to the same dose.
The objective of radiation therapy is to kill uterine cancer cells for a maximum probability of cure or palliation with a minimum of side effects. Some women with uterine cancer have hormonal therapy.