
Proper dosing of the radiation requires the expertise of highly trained radiation oncologists, physicists, and dosimetrists such as those available at the lung cancer/thoracic oncology program at rutgers cancer institute of new jersey. It may also be combined with surgery and/or chemotherapy to help increase its effectiveness.
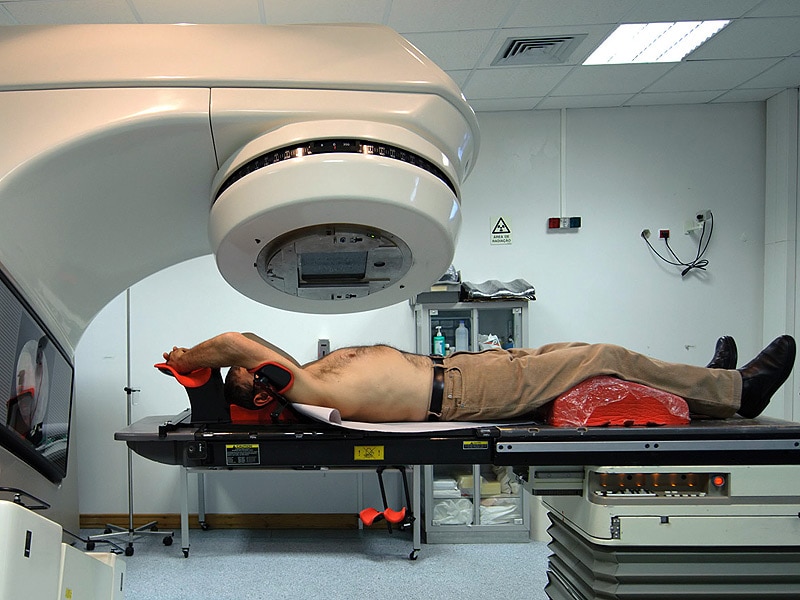
Radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment that uses beams of intense energy to destroy or damage cancer cells and keep them from growing.
Radiation therapy for lung cancer. This type of radiation is used most often when lung cancer has spread to the brain. However, like many other treatments, it can cause certain side effects. It may also be used to aim radiation at small tumors in the lungs when surgery isn�t done.
In the treatment of lung cancer, radiation therapy can be used before surgery to shrink a tumor or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells. Radiation therapy works by directing high. Your healthcare team will consider your personal needs to plan the type and amount of radiation, and when and how it is given.
Radiation therapy, or radiation oncology, involves using targeted, penetrating rays of energy (radiation) to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy for small cell lung cancer. The treatment can be given to cure patients whose lung cancers are confined to the chest but cannot be removed surgically.
As the main treatment (sometimes along with chemotherapy ), especially if the lung tumor can’t be removed because of its size or location, if a person isn’t. Radiation therapy also helps to ease symptoms associated with advanced lung cancer such as breathing problems. Radiation therapy uses radiation beams to damage cancer cells and shrink tumors.
Many patients with lung cancer will be treated with radiation therapy. You may have heard the term “radiation” when discussing lung cancer treatments. Because lung cancer can be present in a large area, it’s not used for every patient.
Radiation therapy for lung cancer. Current progress of radiation therapy in cooperation with the development of physics and biology is remarkable. You may also receive other treatments.
It may also be combined with surgery and/or chemotherapy to help increase its effectiveness. Depending on the stage of small cell lung cancer (sclc) and other factors, radiation therapy is used: Radiation therapy for treatment of lung cancer.
High doses of radiation are used. It’s very effective at controlling or eliminating tumors at specific sites in the body. Radiation therapy for lung cancer can be very effective for destroying cancerous cells and shrinking tumors.
Radiation therapy works within cancer cells by damaging their dna, and inhibiting their ability to grow and divide. Radiation may come from outside the body (external) or from radioactive materials placed directly inside the lung. Radiation is a type of lung cancer treatment designed to only target cancer cells and not affect other parts of the body.
The types of radiation therapies we use to treat lung cancer include: Radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment that uses beams of intense energy to destroy or damage cancer cells and keep them from growing. People with untreated lung cancer will eventually develop tumors in other organs, such as the brain, liver, or kidneys.
When cancerous cells try to divide, they realize their dna has. Radiation therapy for lung cancer also known as radiotherapy, radiation therapy is the use of targeted radiation to kill or damage cancer cells so they cannot grow, multiply or spread. Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
A tumor in or near the lungs can move as you breathe, making it difficult to accurately target with standard radiation. Specifically, when healthy cells are exposed to radiation, they can be damaged in the same way that cancerous cells are, leading to adverse effects at the site of exposure. External beam radiation therapy for lung cancer.
Most people with lung cancer have radiation therapy. Radiation therapy kills cancer cells or slows their growth by damaging their dna. Adaptive radiation therapy (art) allows for modification of a treatment plan with the goal of improving the dose distribution to the patient due to anatomic or physiologic deviations from the initial simulation.
To treat the tumor and lymph nodes in the chest. Radiation therapy is one of the most important modalities for the treatment of lung cancer. Radiation therapy is often combined with chemotherapy to treat lung cancer.
Radiation oncology is a medical specialty that in many cases can be the single most effective method to treat lung cancer. In limited stage sclc, it might be used at the same time as chemotherapy. As a result, the tumor may not receive enough radiation, and healthy tissue near the tumor may be damaged.
Most often, we recommend radiation therapy after lung cancer surgery. Lung cancer treatment is constantly evolving due to technological advances in the delivery of radiation therapy. Stereotactic radiation therapy is a type of external radiation that uses high doses of radiation aimed at a tumor from many different angles.
Proper dosing of the radiation requires the expertise of highly trained radiation oncologists, physicists, and dosimetrists such as those available at the lung cancer/thoracic oncology program at rutgers cancer institute of new jersey.