The prognosis of [1] patients with ipf is poor, and there is no curative treatment. Besides, current studies revealed the impact of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis on the clinical outcome of lung cancer patients , but a comprehensive evaluation hasn’t been performed yet.
Pulmonary fibrosis is a disease marked by scarring in the lungs.
Pulmonary fibrosis lung cancer. In this paper, we report a case of pulmonary fibrosis with lung cancer following single lung transplantation. Gap stage introduction the incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf), a debilitating fibrotic lung disease of unknown origin, is steadily increasing, as is the mortality associated with the condition. The incidence and clinical factors related to development of lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) are unclear.
Pulmonary fibrosis is one form of interstitial lung disease. Patients with ipf have a median survival of 3. Although chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer (sclc) patients with iip may result in the exacerbation of iip, these patients commonly receive chemotherapy.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) was reported to be associated with increased risk of lung cancer as a result of the occurrence of atypical or dysplastic epithelial changes in fibrosis which progressed to invasive malignancy. Also, the prevalence of the tumor region involved from the highest to the lowest was estimated to be in the rll, lll, rul and lul regions. Interstitial lung diseases (ilds) comprise over 200 parenchymal lung disorders.
The prognosis of [1] patients with ipf is poor, and there is no curative treatment. The information here can be helpful to anyone facing one of the many types of pulmonary fibrosis, including the most commonly diagnosed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf). Pulmonary fibrosis is a disease where there is scarring of the lungs, which makes it difficult to breathe.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is defined as a specific form of chronic, progressive fibrosing interstitial pneumonia of unknown cause, occurring primarily in older adults, and limited to the lungs. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is characterized by progressive parenchymal fibrosis of unknown etiology and is associated with poor prognosis 1. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is a form of chronic, progressive, fibrosing interstitial pneumonia of unknown etiology [ 3 ].
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is a form of chronic progressive interstitial pneumonia with a median survival of 3 to 5 years. This condition occurs when that lung tissue becomes thick and stiff for unknown reasons. The use of immunosuppressants reduces the lung cancer survival rates of patients that receive lung transplants, and there are currently no effective treatments available.
The most common is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or ipf. Over time, these changes can cause permanent scarring in the lungs, called fibrosis, that make it progressively. Pulmonary fibrosis and lung carcinoma:
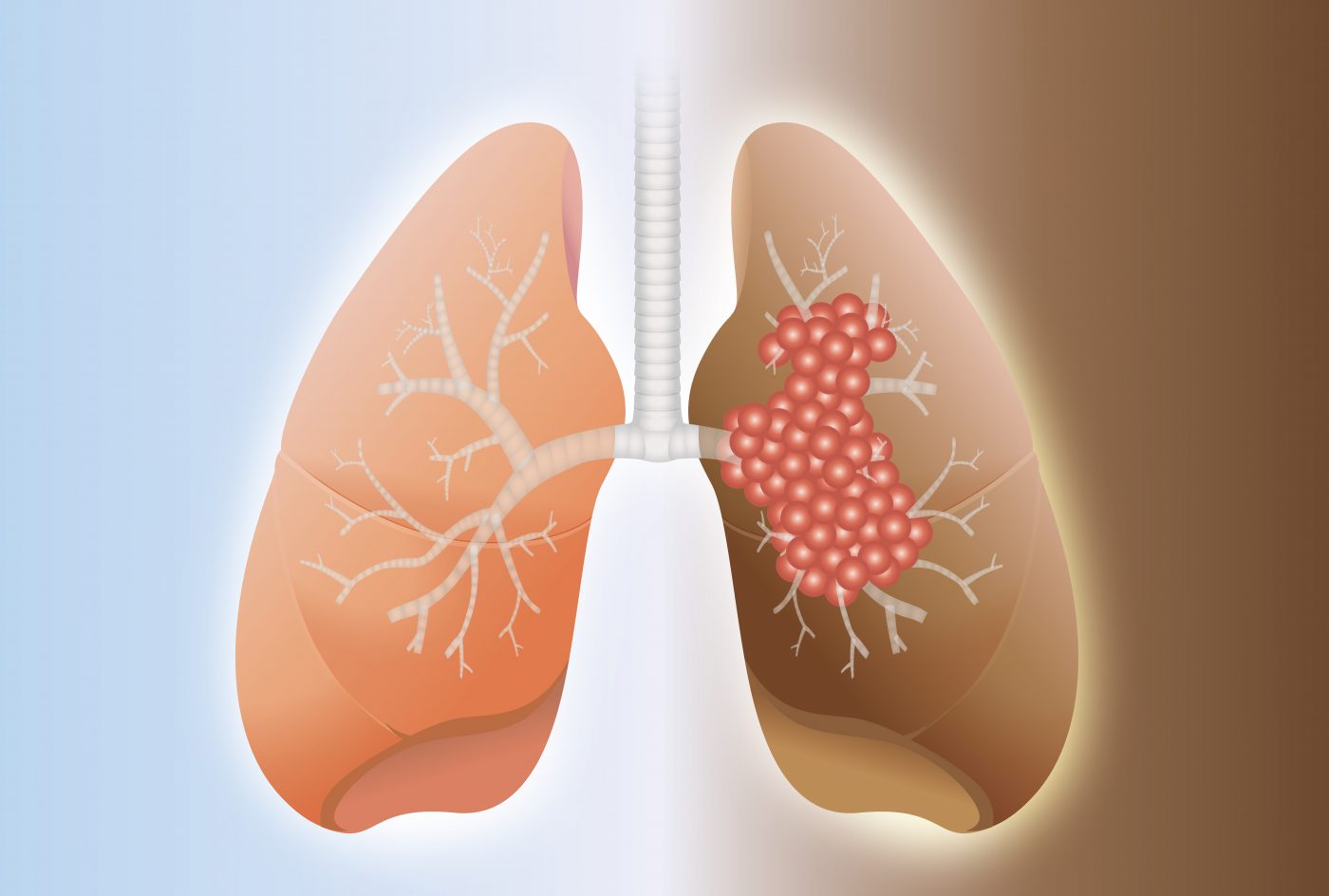
A high proportion manifests as fibrotic ild (fild). The highest involvement location of lung cancer in ipf patients was in the peripheral. The incidence of lung cancer (lc) is markedly increased among patients with ipf ranging from 4.4% to 48%.
Pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic disease whose causes are very varied. A comparative study of metaplastic epithelia in honeycombed areas of usual interstitial pneumonia with or without lung carcinoma. A secondary lung transplant was performed 8 months later.
Among them, fibrosing ilds, especially idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, are associated with a poor prognosis, whereas some other ilds, such as sarcoidosis, have a much better prognosis. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is a serious chronic disease that affects the tissue surrounding the air sacs, or alveoli, in your lungs. Pulmonary fibrosis is a disease marked by scarring in the lungs.
According to the current pathogenic hypothesis, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is the result of chronic damage of the alveolar epithelium leading to a series of events responsible for abnormal tissue repair and the profound changes of the alveolar structure that characterize this disease [ 1 ]. Recent scans showed no progression of the cancer. It causes inflammation and scarring of the lungs.
Submit your manuscript with us. The highest and lowest stage of lung cancer in ipf patients was estimated at iii and ii, respectively. The relative risk of ipf patients developing lc is approximately eight times higher than that of the general population 8 , and the reported prevalence of lc in patients with ipf ranges from 2.7% to 31.3% 6 , 9.
With a gradually increasing worldwide prevalence and a mortality rate exceeding that of many cancers, ipf diagnosis and management are critically important and require a comprehensive multidisciplinary approa. The cancer was treated with radiation in february, whole brain and targeted lung (one tumor, one lung, one lobe). Risk and benefit analysis of pulmonary resection.
View article pubmed/ncbi google scholar 52. This type of pulmonary fibrosis has no known cause. In that situation, the cancer will develop in the area of major fibrosis.
Besides, current studies revealed the impact of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis on the clinical outcome of lung cancer patients , but a comprehensive evaluation hasn’t been performed yet. Pulmonary fibrosis is a complicated, chronic illness that can derive from many different causes. Pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer:
The aim of this study was to elucidate the cumulative incidence, risk factors, and clinical characteristics of lung cancer in ipf. This article has been cited byother articles in pmc. Patients with combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (cpfe) have been suggested to have an increased risk of lung cancer.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) is a chronic fibrotic lung disease of unknown etiology. Many diseases can cause pulmonary fibrosis, but in half of the cases the cause remains unknown. There are many different types of pulmonary fibrosis.
Lung cancer is a common comorbidity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (ipf) and has poor outcomes. Lung cancer (lc) is a frequent complication of fild.