Proton therapy treatment is an effective and desirable option to treat lung cancer. Lung and thoracic cancers we treat with proton radiation therapy include
Proton radiotherapy is a gentle cancer treatment method with minimal side effects.
Proton therapy for lung cancer. Proton therapy spares healthy normal tissue and nearby organs. Proton therapy is a form of radiation therapy that, for some lung cancer patients, allows for greater sparing of their organs from the effects of radiation exposure. It can also be used to treat cancers that are close to important structures in the body.
It delivers a higher dose of radiation to a very precise, targeted treatment area in the lungs, resulting in higher success rates, fewer side effects, and the ability to protect healthy lung tissue. Surgery and radiation are the primary curative modalities to treat lung cancer. 1 physicians and scientists, including those at the northwestern medicine proton center, work tirelessly on lung cancer treatments that improve outcomes while minimizing risks and side effects.
As a result, protons can minimize side effects such as lung inflammation (pneumonitis) or scarring (fibrosis), difficulty swallowing, heart complications, hospitalizations, and other side effects that are commonly seen with conventional lung cancer treatment. Proton therapy treatment is an effective and desirable option to treat lung cancer. Proton therapy is a type of radiation that can be stopped at a prescribed depth in tissue, whereas conventional radiation continues beyond the tumor.
Proton therapy for lung cancer is now considered a treatment option for patients whose cancer is limited to the chest. One of proton therapy’s greatest benefits is that its focused treatment enables physicians the ability to administer the exact amount of radiation they want at the exact place they want it. Using proton technology’s advanced image guidance and ability to precisely target tumors in the lungs, our specialists can deliver powerful radiation dosages with optimal accuracy, sparing critical nearby structures, such as the esophagus, lung, heart and spinal cord.
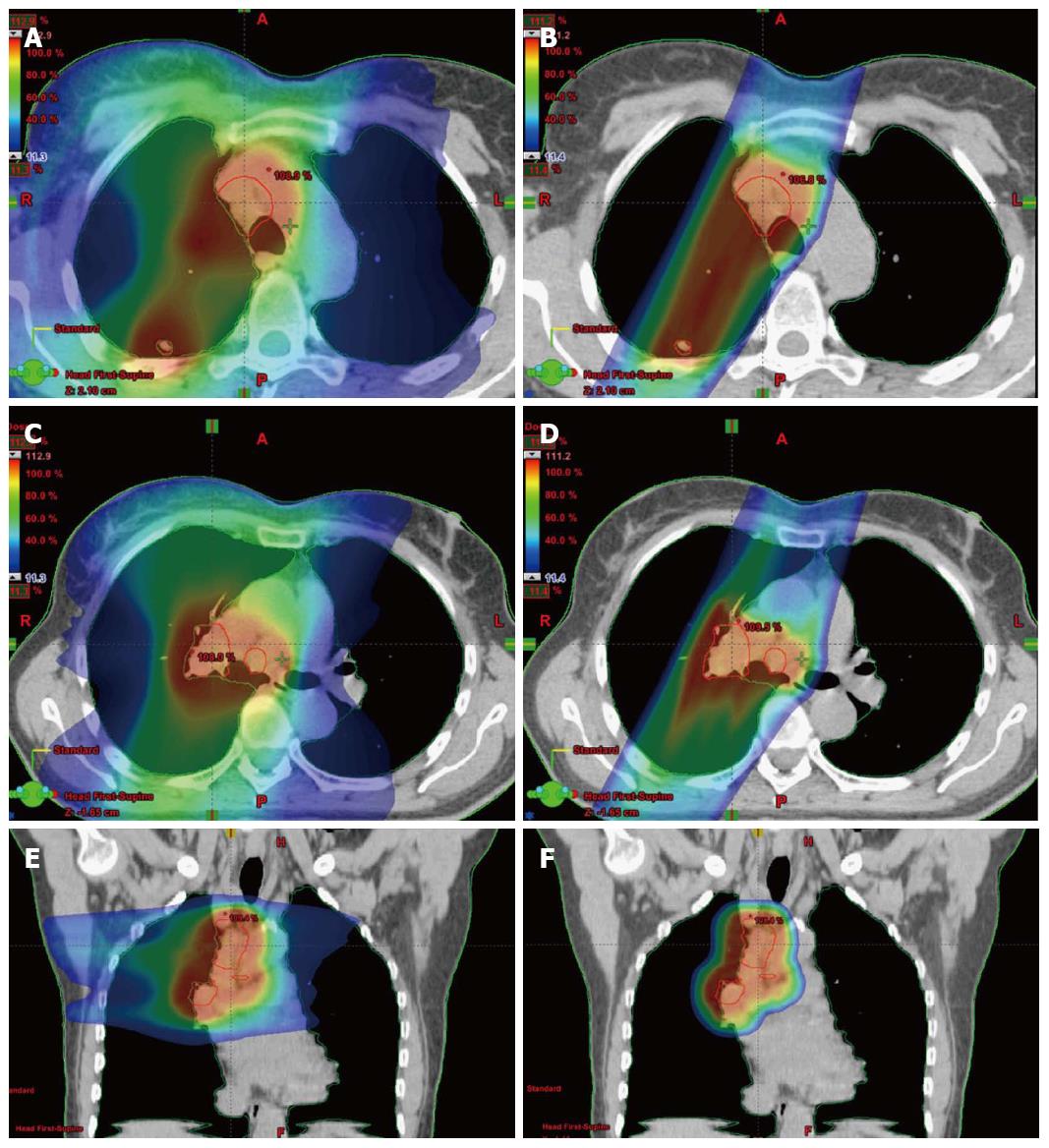
Proton therapy concentrates a high dose in the tumor. More than 50% of cancer patients were reported to undergo radiotherapy during their whole disease treatment [].due to the dosimetric benefits of proton, the clinical use of proton therapy for cancers is dramatically growing and more than 79 operational facilities worldwide by 2019 [].currently, proton therapy is being used for the radiation therapy of pediatric cancer,. In lung cancer, proton therapy, when compared with photon treatment, has significant dosimetric advantages, with reduced dose to normal lung, esophagus, heart and other oars.
It allows for accurate targeting of the proton beam to the target area (at the location of the original tumor) in the lung, thus minimising exposure of surrounding tissues and organs to radiation. Because of the treatment’s accuracy, a large amount of healthy tangential tissue, organs and nerves are spared unnecessary exposure. Proton beam therapy is only suitable for a small number of people.
Lung cancer accounts for almost 13 percent of all cancer diagnoses, with an estimated 224,390 new cases in 2016 alone. That’s where proton therapy has the advantage for many lung cancer and other thoracic cancer patients. Proton therapy is a type of external beam radiotherapy that uses ionizing radiation.
3 additionally, proton therapy can be used to deliver more radiation to the tumor to improve the outcomes for lung cancer. Proton therapy enables physicians to treat lung cancer while minimizing the risk to surrounding healthy tissues and organs. This is the first time this type of radiotherapy.
Proton therapy is more accurate and precise than other kinds of radiation. Proton therapy is one method of treatment to come out of. Proton therapy is not appropriate for every type of cancer.
The machines and equipment for proton therapy are very complex and expensive to make and operate. Proton beam therapy is a type of external beam radiotherapy. Pencil beam scanning capabilities provide precise doses of radiation to targeted areas.
Studies show some lung cancer patients can receive higher therapeutic doses with fewer radiation side effects. Proton radiotherapy is a gentle cancer treatment method with minimal side effects. Less radiation to your heart, lung, and esophagus
Proton therapy can be a valuable form of radiation treatment for many patients with lung cancer. In proton therapy, medical personnel use a particle accelerator to target a tumor with a beam of protons. Of the 110 patients, 17 were diagnosed with ild.
Patients treated with proton therapy may have increased tolerance for chemotherapy. Benefits of proton therapy for lung cancer. Proton beam therapy (pbt), through its characteristic bragg peak, has the potential to decrease the toxicity of radiotherapy, and, subsequently improve the therapeutic ratio.
It is best suited for cancers in sensitive areas, where other treatments might damage surrounding healthy cells. Lung and thoracic cancers we treat with proton radiation therapy include Once lung cancer is diagnosed, local techniques are generally used in the very earliest stage of lung cancer treatment.
These charged particles damage the dna of cells, ultimately killing them by stopping their reproduction and thereby eliminating the tumor.