
The bones of the axial skeleton are the predominant site of metastasis in most men with metastatic prostate cancer ( image 1 ), and these lesions can cause pain, debility, and/or functional impairment. These symptoms can cause severe discomfort and disability.
4 in the early stages of advanced prostate cancer, malignant cells detached from the primary tumor migrate locally, invade blood or lymphatic vessels, and.
Prognosis of prostate cancer with bone metastases. Spinal cord compression can result in nerve damage, which can. Bone metastases from lung cancer are usually lytic. Bones are the most common site of prostate cancer metastasis, occurring in 85%90% of patients with metastatic prostate cancer.
A unique case of isolated pulmonary metastases with exsanguinating hemoptysis is described to illustrate the dramatic response to androgen deprivation. The bone microenvironment is a favorable metastatic niche. Uncharacteristic aggressiveness of the disease;
Pain or stiffness in the neck or. Promptly treating prostate cancer bone metastases with the newest medication can help change a man’s prognosis dramatically, tagawa says. Patients with advanced prostate cancer can have cancer cells that have spread to their bones, called bone metastases.
It can lead to thirst, excessive fatigue, confusion, constipation, drowsiness, nausea, and lack /loss of appetite. Various treatments for bone metastases can help relieve symptoms and prolong life. The clinical manifestations and diagnostic assessment of bone metastases in men with prostate cancer are reviewed here.
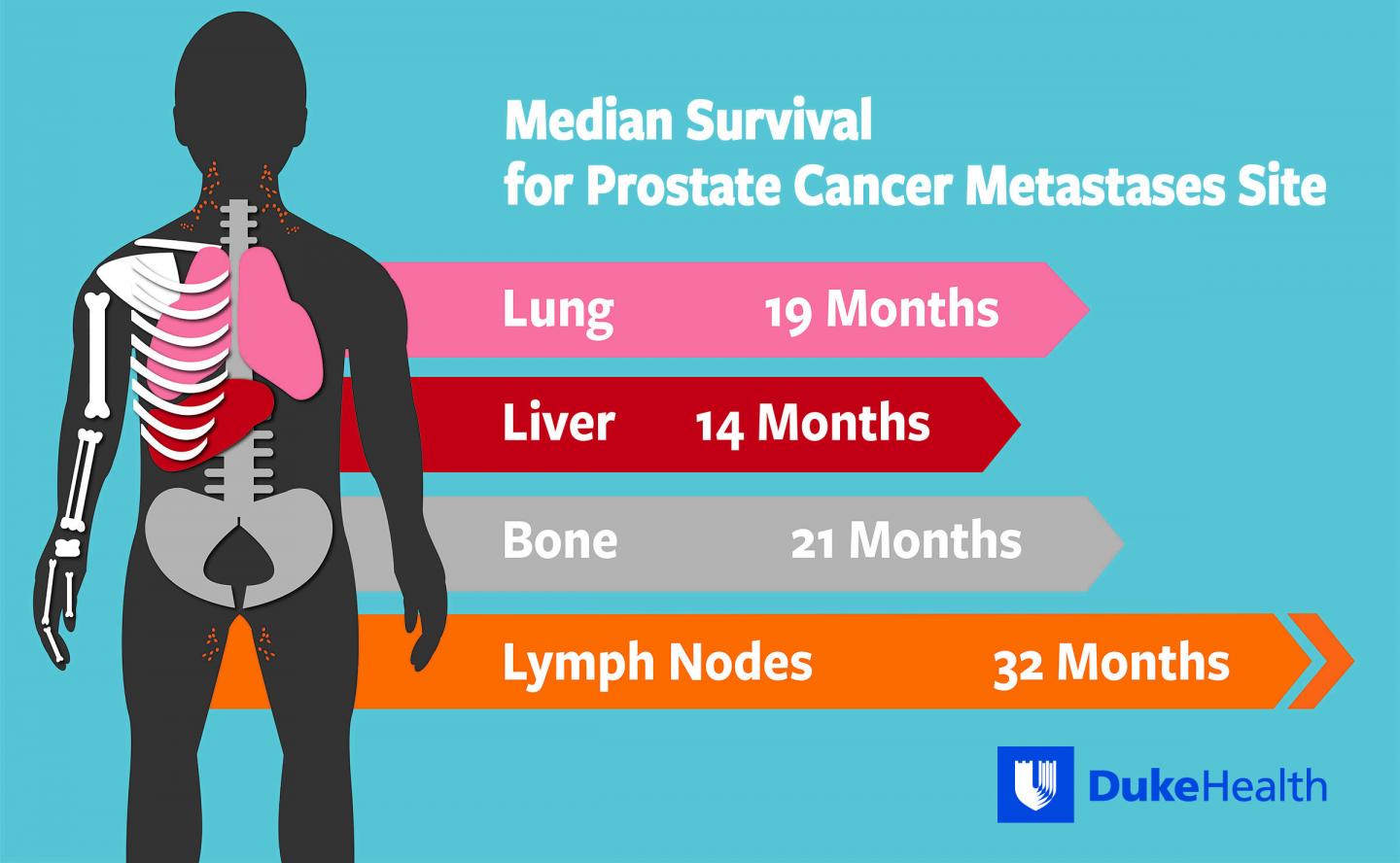
Prognosis of prostate cancer and bone metastasis pattern of patients: This average survival rate represents stage iv prostate cancers that have metastasized (spread) beyond nearby areas to lymph nodes, organs or bones in other parts of the body. It is important to remember that this secondary tumor is made up of.
Once prostate cancer has spread to the bones, symptoms can include: Prostate cancer (pca) prognosis and clinical outcome is directly dependent on metastatic occurrence. The bones of the axial skeleton are the predominant site of metastasis in most men with metastatic prostate cancer ( image 1 ), and these lesions can cause pain, debility, and/or functional impairment.
There’s no cure for metastatic bone. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have any symptoms. 4 in the early stages of advanced prostate cancer, malignant cells detached from the primary tumor migrate locally, invade blood or lymphatic vessels, and.
“there are men who do well for decades,” he says. Having had the chance to grow due to negligence on the part of the patient; When prostate cancer cells have entered the bloodstream and traveled to the bone, you may notice bone pain, weak bones , spinal cord compression, stiffness, or pain in the hip, thighs or back.
Bone metastases can weaken your bones and lead to symptoms like bone pain. Therefore, bone cancer and bone metastases are not the same. Once in the blood, the cancer cell can travel to the bone and form a new tumor.
With bone metastases, life expectancy depends on the type of primary cancer, your response to treatment, bones affected, severity of bone damage, etc. Prostate cancer cells from the primary tumor can break away and get into the bloodstream. Once the cells settle in the bone, they start to interfere with the bones normal health and strength, often leading to bone pain, fracture, or other complications that can significantly impair a mans health.
Patients with advanced prostate cancer can have cancer cells that have spread to their bones, called bone metastases. You also may have higher levels of calcium in the blood, which occurs as cancer cells replace normal bones. If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it nearly always goes to the bones first.
32 in cancer patients, development of bone pain usually is considered to be highly suggestive of bone metastases. These symptoms can cause severe discomfort and disability. Indeed, prostate cancer has an affinity to metastasize to bone, which provides a matrix rich in factors that stimulate the growth of tumor cells and promotes a vicious cycle of metastases and bone pathology.
The symptoms you have will depend on where the cancer has spread to. Theoretically, any sites of bone can be affected by the cancer. When prostate cancer spreads, the bones are typically the first area affected.
Metastatic prostate cancer in the bones is the embodiment of late stage advanced prostate cancer. Stiffness or pain in the hip, thighs, or back. Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as fatigue (extreme tiredness), bone pain, and problems urinating.
Bone pain is the most common type of pain from cancer, is poorly localized, worse at night, not necessarily relieve with sleep or lying down. The prognosis (outcome) of cancer that has spread to the bones varies according to many factors. These may include surgery, radiotherapy & brachytherapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, pain relief, and biphosphonates (a kind of procedure to protect the strength of bone).
Weak bones that are more likely to fracture; Bone metastasis is a common complication in patients with advanced stage prostate cancer and might even be found already at first clinical diagnosis [1, 2].depending on the extent of spread, bone marrow function might become compromised, resulting in anaemia und thrombocytopenia [3, 4].prognosis after onset of anaemia und thrombocytopenia is not well. As an example, consider a patient with prostate cancer.
A bone scan index >3.5% was also associated with a high. 5 the pain associated with bone metastasis could be either of inflammatory or mechanical origin. Bone metastasis can be painful and can cause other problems, such as fractures (breaks), spinal cord compression (an area of cancer is pressing on the spinal cord), or high blood calcium levels, which can be dangerous or even life threatening.
But hip area, thing bone /long bones, and spine are some common sites of bone that often affected by the metastasis of prostate cancer! There are many different types of treatments that can be involved to treat and manage the advanced prostate cancer with bone metastases.