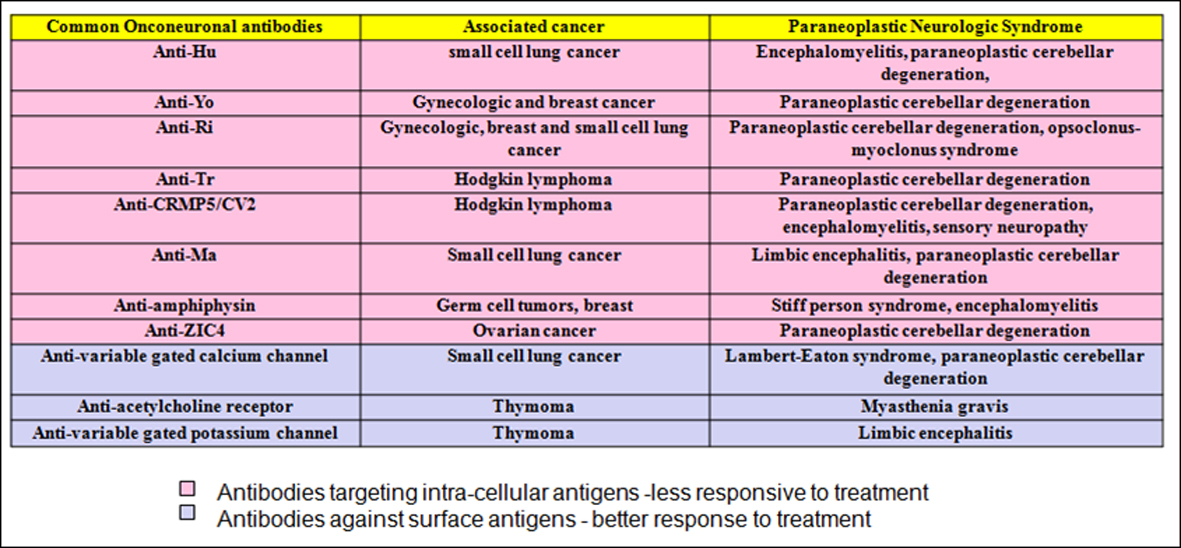
Most paraneoplastic syndromes are caused by small cell lung cancer (sclc). Paraneoplastic syndromes refer to groupings of symptoms that occur in patients with malignant neoplasms that cannot be readily explained by local invasion or distant metastasis of the tumor, or the elaboration of hormones indigenous to the tissue of origin of the neoplasm.
The cancers more often associated with paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis are cancers of the lung and testis and tumors of the thymus (thymoma) although other cancers can also be involved.
Paraneoplastic syndrome lung cancer. Paraneoplastic syndromes arise most commonly with small cell lung cancer as well as gynecological and hematological malignancies. Researchers have discovered a long list of paraneoplastic syndromes that have occurred in people with lung. Paraneoplastic syndromes may affect diverse organ systems, most notably the endocrine, neurologic, dermatologic, rheumatologic, and hematologic systems.
The paraneoplastic syndrome occurs in 20% of people with cancer. We performed an analysis of the data of 1,669 patients with lung cancer aged between 24 and 87 years, among whom there were 89% of men. Paraneoplastic syndromes refer to groupings of symptoms that occur in patients with malignant neoplasms that cannot be readily explained by local invasion or distant metastasis of the tumor, or the elaboration of hormones indigenous to the tissue of origin of the neoplasm.
Paraneoplastic syndromes can affect multiple systems and have a diverse presentation. Paraneoplastic syndromes clinical syndromes caused by underlying malignancy mediated by humoral factors secreted by tumor cells or by responses to tumor antigen associated with many types of lung cancer can be the first manifestation of disease or disease recurrence 10% lung cancer patients present with a paraneoplastic syndrome Sometimes the first sign of cancer in a patient is the
Symptoms identical to paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis may occur without cancer; Paraneoplastic syndromes (pnss) result in changes to bodily structure or function that are not directly related to the primary tumor or metastasis. Up to 16% of patients with small cell lung.
This review focuses on recently published literature on paraneoplastic syndromes associated with lung cancer, including humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy, autoimmune paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes, neuromuscular disorders, and. The most common cancers with which paraneoplastic syndrome occurs are breast cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, ovarian cancer, stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, lymphomas, and leukaemia. 34 rows a paraneoplastic syndrome is a syndrome that is the consequence of cancer in the.
Most paraneoplastic syndromes are caused by small cell lung cancer (sclc). The cancers more often associated with paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis are cancers of the lung and testis and tumors of the thymus (thymoma) although other cancers can also be involved. Sclc, also known as oat cell lung cancer, is known to be a more aggressive lung cancer;
Pns developed in almost 1 in 10 patients with lung cancer and it may be an indicator for the diagnosis of lung cancer and it can be seen during later stages of cancer or at the time of cancer recurrence. Some examples are given below 1,2: In the case of lung cancer, they are mostly found either in squamous lung cells or small cell lung cancer.
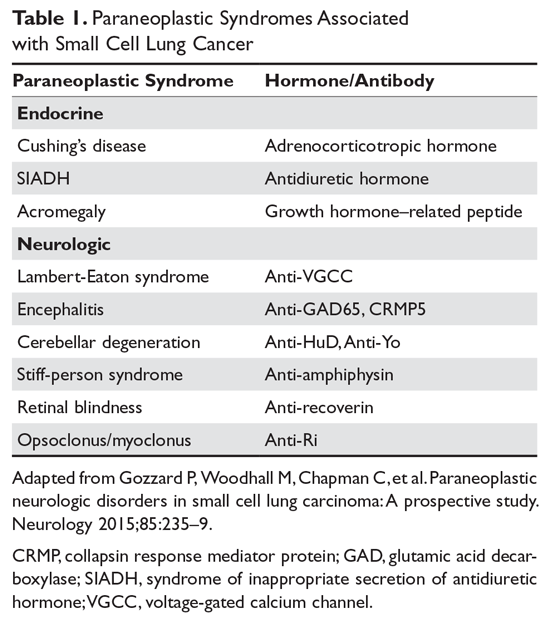
Lung cancer and paraneoplastic syndromes. Lung cancer and paraneoplastic syndromes. One of the most common paraneoplastic syndromes associated with lung cancer is the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (siadh) secretion.
Syndromes in lung cancer paraneoplastic syndromes are common in lung cancer, and may be the first manifestation of the disease or its recurrence. Cell lung cancer (nsclc) or small cell lung cancer (sclc) (knop, 2005). The term paraneoplastic syndrome refers to the ability of some tumors to produce signs and symptoms at a distance from the site of the primary tumor or its metastases.
Lems is the most common neurological paraneoplastic syndrome in small cell lung cancer (sclc). Paraneoplastic syndromes may develop before the diagnosis of carcinoma is made. Amitavasoya d.o., facoi, fccp, faasm christiana care pulmonary associates clinical assistant professor of medicine sidney kimmel medical college of thomas jefferson university rowan university school of osteopathic medicine.
Paraneoplastic lems is almost always associated with sclc. Annual incidence of lems is 0.6 case per million, and prevalence is 2.8 cases per million in the us. Large cell carcinoma of the lung (10% to 15%) is the term reserved for those carcinomas not meeting…
Paraneoplastic syndromes have been estimated to affect 10 percent of people with lung cancer. The most commonly associated malignancies include small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, gynecologic tumors, and hematologic malignancies. To study the nature of different variants of paraneoplastic syndrome (pnps) in lung cancer, taking into account the features of the tumorous process and the complications of radiochemotherapy.
These are most commonly caused by tumor production of small molecules such as hormones or cytokines. Lung cancer, particularly small cell lung cancer, is the most common malignancy causing paraneoplastic syndromes. However, lems associated with nsclc is also reported.
Paraneoplastic syndromes in dogs and cats. The group of diseases occur due to the immune system. Small cell lung cancer is more often associated with these syndromes.
Paraneoplastic phenomena are not related to the direct invasion, obstruction, or metastasis. Small cell lung cancer is especially notorious for its numerous and distinct paraneoplastic syndromes. Paraneoplastic syndrome is a group of rare autoimmune diseases that can occur due to lung cancer, especially small cell lung cancer (sclc).
Paraneoplastic syndromes in lung cancer. Paraneoplastic syndromes associated with small cell lung cancer (sclc) include. Paraneoplastic syndromes may be most common in lung cancer compared to other types of cancer.