Overall, interest in genetic testing for ovarian cancer was very high. This means a known mutation has been found, and you will be provided with a letter detailing exactly what that mutation is.

This study surveyed 232 patients who underwent genetic counseling for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer to examine the impact of panel gene testing on psychological outcomes, patient understanding, and utilization of genetic information.
Ovarian cancer genetic test. Genetic testing is available for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. This test is designed to help people who may be at risk for ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and other forms of cancer by providing them with the means to assess their risk and make informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment of their cancers. When you’re at increased risk.
Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. The ovarian cancer comprehensive panel examines 19 genes associated with an increased risk for hereditary ovarian cancer. The problem with ovarian cancer is that there is no screening period.
If a family member with cancer is tested and found to have an abnormality in one of these genes, other relatives with or without cancer may be tested for the specific alteration identified. If someone with a significant family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer is interested in genetic testing, it is recommended that a relative who has had breast or ovarian cancer be tested first. This means that someone in your medical team will speak to you about genetic testing during one of your oncology appointments.
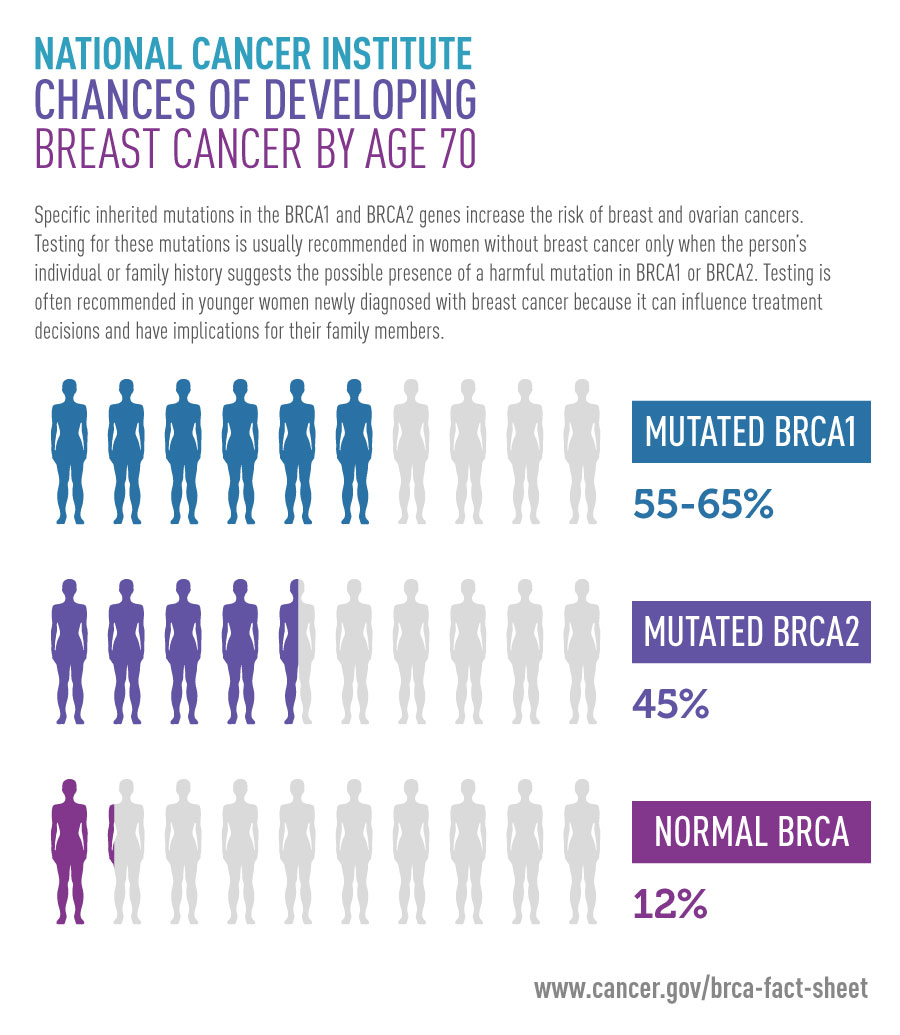
Most breast and ovarian cancer is not caused by inherited mutations, so genetic testing will not help most women with a family health history of breast and ovarian cancer. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome due to mutations in the brca1 or brca2 gene is the most common known cause of hereditary ovarian cancer. It is now becoming routine to test for germline mutations in the brca1 and brca2 genes,.
If testing indicates you’re at increased risk for ovarian cancer, one of our counselors can help you clarify and better. Genetic testing can help people identify risk factors for developing certain conditions, including ovarian cancer. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer and can spread.
As genetic testing becomes less expensive and more widely available, scientists will be better able to determine which variant is most common within a specific population. Lisa and other female members of her family all underwent genetic testing at uconn health to determine if they were at risk for ovarian cancer. Or a blood relative may have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, or diagnosed with breast cancer before age 50.
Yet a minority of respondents (22%) actually offered brca testing directly to their. A positive test result may bring relief by resolving uncertainty regarding future cancer risk and may allow. Ovarian cancers were previously believed to begin only in the ovaries, but recent evidence suggests that many ovarian cancers may.
This study surveyed 232 patients who underwent genetic counseling for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer to examine the impact of panel gene testing on psychological outcomes, patient understanding, and utilization of genetic information. What a positive result means if your predictive genetic test result is positive, it means you have a faulty gene that raises your risk of developing cancer. Genetic aberrations impact ovarian cancer prognosis and treatment decisions.
It scans your dna to pinpoint whether you have a. There is no effective screening tool, so if you don’t recognize the patient at risk and undertake risk reduction measures, just monitoring them will not prevent them from getting the disease. Epithelial ovarian cancer) are often offered access to genetic testing for mutations in their brca1 and brca2 genes, even if they have no family history of ovarian cancer.
It can take 4 to 8 weeks or longer to get the result. For example, the following cancer syndromes are associated with an elevated risk of ovarian cancer and several other types of cancer: The practices of oncologists surrounding genetic testing for breast and ovarian cancer are summarized in table 1.
For ovarian cancer, another common gene is brip1. This usually means having a very strong family history of early onset breast and particularly ovarian cancer. Because of this, molecular profiling is important in guiding treatment strategies and counseling patients.
As the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer (oc) moves further into personalised medicine, the importance of determining the presence or absence of inherited mutations in cancer susceptibility genes has grown. It is performed on a blood sample. Possible results of the testing.
There can be benefits to genetic testing, regardless of whether a person receives a positive or a negative result. The majority of respondents (79%) had discussed genetic testing for breast and ovarian cancer risk with their patients. Myriad genetics offers a test for ovarian cancer called the myriad myrisk hereditary cancer test.
The american society of clinical oncology recommends that all women diagnosed with epithelial ovarian cancer be offered genetic testing for inherited variants in brca1, brca2, and other ovarian cancer susceptibility genes, regardless of the clinical features of. Anticipated uptake of genetic testing for ovarian cancer. The need to increase the number of ovarian cancer patients that can potentially benefit from treatment with targeted therapies, such parpis, has significantly increased the need for tumor testing through which additional genetic changes, which can predict sensitivity to parp inhibition, can be identified.
There are a few stages to having a genetic test. Overall, interest in genetic testing for ovarian cancer was very high. Tumor testing in ovarian cancer.
This means a known mutation has been found, and you will be provided with a letter detailing exactly what that mutation is. Ovariangene is a genetic test for women diagnosed with or at risk of ovarian cancer which examines the dna code of ten genes known to cause an increased risk of ovarian cancer. Certain mutations, such as those affecting the brca1/2 genes, serve as biomarkers and have been shown to increase the risk of ovarian cancer, as well as predict outcomes to specific treatments.
In many places genetic testing is done by the same team and in the same place as your ovarian cancer treatment (the oncology clinic). Most women said they would ‘probably’ or ‘definitely’ take up an offer of genetic testing (84.9 %, n = 734), which increased to 88.3 % (n = 819) if the test also informed about breast cancer risk. Although ovarian cancer is the 8 th most common cancer in women, genetic testing for brca mutations is not yet easily accessible in many countries.
Genetic testing will not identify the cause for some hereditary breast and ovarian cancers, because the. Research has evolved significantly beyond the initial.