However, it has been reported in the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, urogenital region, head, neck and the gynecologic tract among others. The diagnosis and treatment of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma are controversial, difficult, and clearly still evolving.
Prognosis for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) is poor, similar to that of small cell carcinoma.
Large cell neuroendocrine cancer. Prognosis for large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) is poor, similar to that of small cell carcinoma. Necs include small and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, while nets include typical and atypical carcinoids. Actuarial survival for 2 groups was not significantly different.
The large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) of the lung was first reported in detail by travis et al. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) of the lung is a rare pulmonary tumor, having similar natural history and management strategy as small cell lung cancer. The morphology of lcnec is similar to that of small cell lung cancer and large cell carcinoma, and about half of the cases present with the endometrioid adenocarcinoma.
Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma was first proposed by travis et al. The diagnosis and treatment of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma are controversial, difficult, and clearly still evolving. Should be distinguished from atypical carcinoid, basaloid squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, although diagnosis can be.
Recently my dad was diagnoseed w stage 4 large cell neuroendocrine. Diagnosing this particular entity can be hampered by the limitations and restrictions imposed by its own definition in the current who classification. Based on clinical pathology, large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) is defined as a large cell expressing the neuroendocrine markers, cga, syn and neural cell adhesion molecule (cd56).
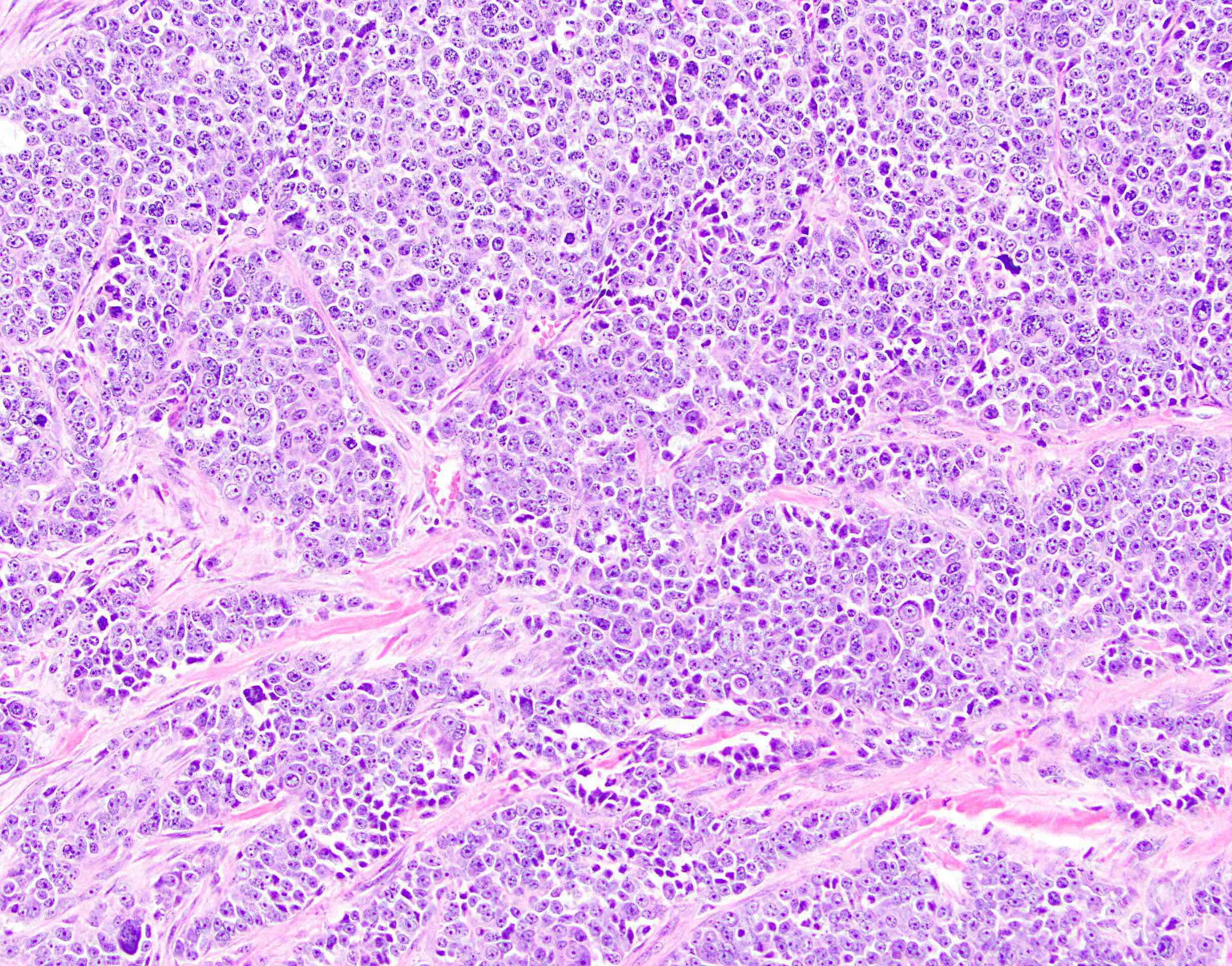
When examined by a pathologist under the microscope, the tumor consists of large neuroendocrine cells. 1 hgnet is a rare tumor with unclear clinicopathologic features and poor mortality given the high rate of metastasis. A rare form of neuroendocrine lung cancer is called large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
In 2004, the world health organization (who) classified lcnec as a variant of large cell carcinomas. It is also classified as a pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor. In 1991 and subsequently classified as hgnet by the world health organization (who) international histological classification of tumours.
Pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) is a subtype of lung cancer with neuroendocrine morphology, neuroendocrine differentiation on immunohistochemistry, a high mitotic rate (>10 mitosis·2 mm −2) and nonsmall cell cytological features [].lcnec is rare and accounts for ∼3% of all lung cancers, but the proportion of lung. Extrapulmonary lcnec rarely occurs, and. Epidemiology the incidence peaks around the 6th decade 6.
This cancer looks and acts like sclc, except that the cancerous cells themselves are larger, and it is treated in much the same way as sclc. Poorly differentiated lcnec of the endometrium is a very uncommon tumor representing only 0.8% of endometrial cancers and they are considered particularly aggressive neoplasms with a tendency for early metastases and poor outcomes. This is another aggressive type of neuroendocrine tumor that accounts for between 0.1 percent to 1 percent of all gastrointestinal tumors.
The most common site of origin for lcnec is the thorax; Therefore, the management of brain metastases in these patients has mirrored that of sclc through the use of whole brain radiation therapy (wbrt). The average tracking is 89 months.
Due to the rarity of lcnec, there are no large randomized trials that define the optimal treatment approach for either localized or advanced disease [ 1 ]. First described the lcnec type of lung cancer in 1991 characterized by large cells with abundant cytoplasm, necrotic areas, high mitotic rate, and neuroendocrine features (2). It is aggressive and he is undergoing chemo from a facility that only handles cancer and is in a large city.
Small cell lung cancer (sclc) is the most common form of neuroendocrine lung cancer. These complexities in the semantics of diagnostic criteria can puzzle not only the pathologist. The bottom line is that the cellular neuroendocrine carcinoma of large lung cells has a weak prognosis, even at the initial stage, with a survival rate similar to that of small cell lung carcinoma.
However, it has been reported in the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, urogenital region, head, neck and the gynecologic tract among others. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of uterus (lcnec of uterus) is a rare subtype of neuroendocrine endometrial cancer. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) is a variant of large cell carcinoma (travis et al., 1999).
Patients are often male and older with heavy smoking history. There are limited data on the epidemiology and best treatment practices for this malignancy. Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) of the lung is classified as a subtype of large cell carcinoma of the lung.