‘but i heard that mirena decreases your. This possible noncontraceptive benefit could be most beneficial in populations with severely limited access to screening and concomitantly high cervical cancer incidence.
A recent study found that patients using the mirena iud have a 20% increased risk of developing breast cancer.
Iud and cancer risk. In this study, the team gathered information from 11 studies that reported data on iud use and ovarian cancer incidents. Although prior studies have also failed to detect any association between iud use and an increased risk of invasive cervical cancer, this is the first to suggest the possibility of a protective effect of copper iuds on this risk. From odd ratio method with 2 x 2 cross tabulation can be known level of cancer risk of respondents who use iud as well as variables that have contribution increase cervical cancer risk that was status of respondent as passive smoker.
Researchers have identified how the hormones progesterone and estrogen interact to increase cell. “the reduced risk of ovarian cancer with the use of oral contraceptives is well established,” said. Iuds may reduce ovarian cancer risk by 30%.
Women diagnosed with breast cancer (in situ or invasive) younger than 50 years old. We searched medline, embase, cochrane library, web of science. Iud and risk of ovarian cancer.
Although women with cervical cancer should not undergo iud insertion (u.s. The mirena iud contains a synthetic version of progesterone (progestin), which has long been considered a hormone that raises the risk of some cancers. Iud use may have a protective effect on endometrial cancer risk.
According to a 2011 michigan state university study: ‘but i heard that mirena decreases your. A study published in september 2019 by researchers at the university of colorado anschutz medical campus has linked that the intrauterine device (iud) may be linked to a decrease in ovarian cancer risk.
Mirena iud users could have higher risk of breast cancer. Cancer precautions and the mirena iud. There do not appear to be any research studies indicating an increased risk of breast cancer from using the paragard iud (copper iud), which does not release hormones.
Researchers long have known that various birth control methods, including iuds, reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. This contraceptive method may provide more benefits beyond contraception, but more research is needed in this area. The protective effect of iud may be either, through the intense inflammatory response that leads to other lisosomal and inflammatory actions, which may include cells responsible for early elimination of hyperplastic endometrial epithelial cells or, the more complete shedding of the endometrium.
Women who have ever used an intrauterine device (iud) for birth control may have a 30% lower risk for ovarian cancer. If women want to avoid. Data analysis used statistic method odd ratio.
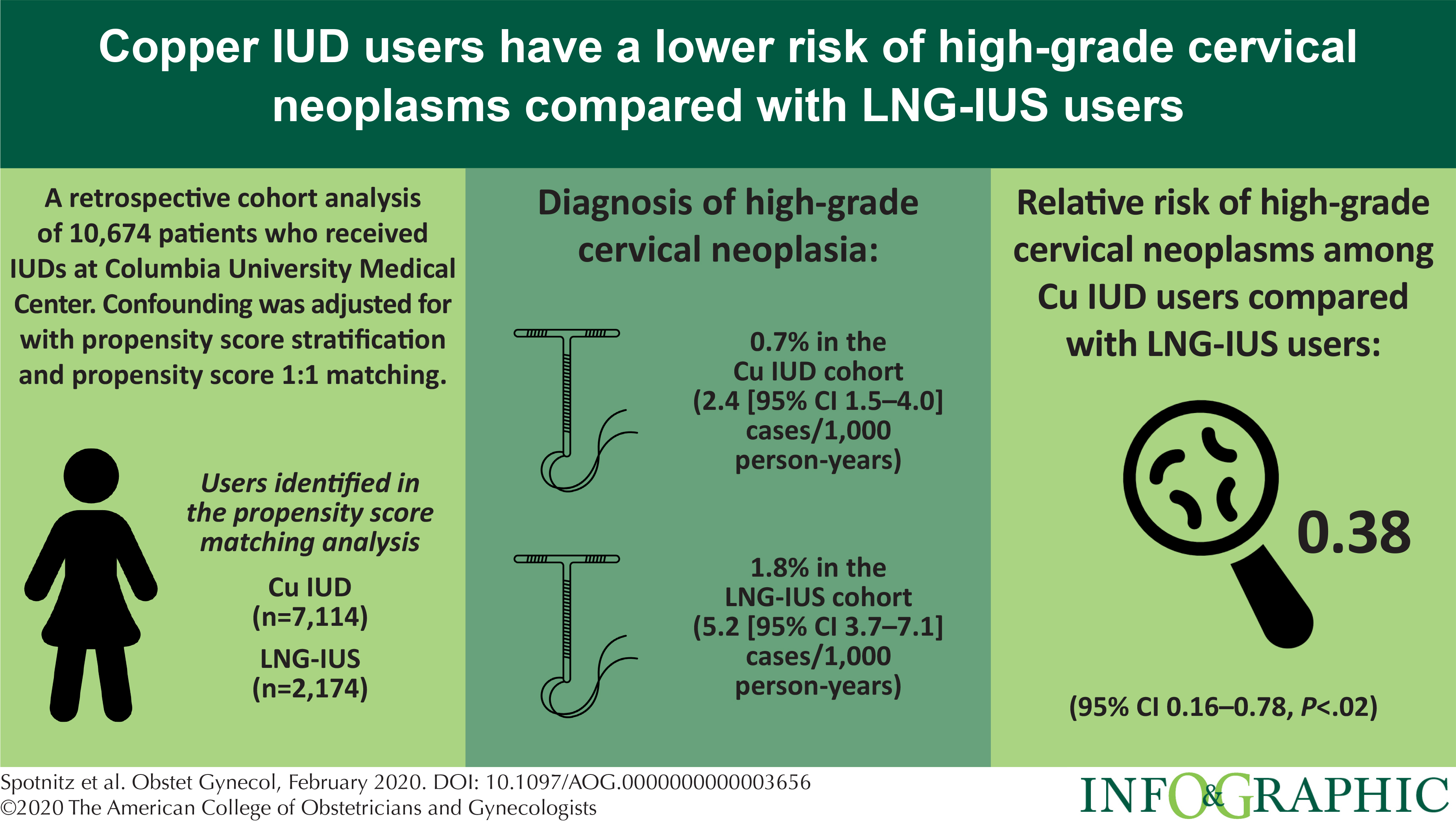
The reduced risk associated with copper iuds increased with increased duration of use. This possible noncontraceptive benefit could be most beneficial in populations with severely limited access to screening and concomitantly high cervical cancer incidence. Study evaluates cervical cancer risks of iuds.
Invasive cervical cancer may be approximately one third less frequent in women who have used an iud. A recent study found that patients using the mirena iud have a 20% increased risk of developing breast cancer. Study evaluates cervical cancer risks of iuds.
When a patient had a history of iud. Previous research has shown that tubal ligation and oral contraceptives decrease ovarian cancer rates. Methods with higher systemic levels of progestin, particularly injectables, did not seem to be associated with increased risk.
The study was published in obstetrics & gynecology. We addressed this relationship through a pooled analysis of data collected in the epidemiology of endometrial cancer consortium. Mec 4) , screening asymptomatic women with cervical cytology before iud insertion is not necessary because of the high rates of cervical screening, low incidence of cervical cancer in the united states, and high likelihood that a woman with cervical cancer.
The natural history of cervical cancer is well established, especially after the discovery of hpv as the cause of cervical cancer.1 recent studies showed surprising findings; Cancer risk is known by using iva method. Across the board, the iud is known to lower risk for many gynecological cancers, including endometrial and ovarian cancer, but with regard to cervical cancer, the latest research suggests the benefit can be significant — as much as a 30% reduced risk.