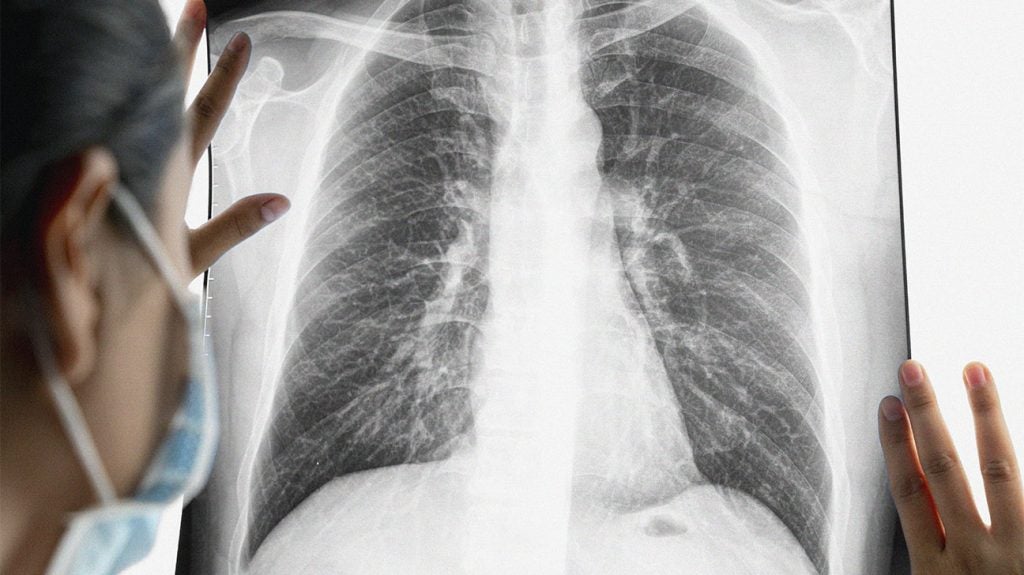
It is characterized by rapid, uncontrolled growth of certain cells in the lungs. We don’t know what causes each case of lung cancer.

A person acquires them during their lifetime.
Is small cell lung cancer hereditary. Paraneoplastic syndrome is a group of rare autoimmune diseases. Small cell lung cancer (sclc) is an aggressive form of lung cancer. If you have a family member with this cancer, you are at higher risk than others to develop the same condition.
It may also be referred to as oat cell carcinoma and, in some cases, is a mixed cell carcinoma. This is often seen in individuals with adenocarcinoma who do not have a history of smoking. The answer is important because it opens the possibility of using targeted therapies based on the genes involved.
Small cell lung cancer, on the other hand, is almost always attributed to smoking tobacco. Hereditary factor can be one of risk factors for lung cancer. In fact, it is quite common to find patients of lung cancer with a family history of the same condition.
About 80% of lung cancer deaths are caused by smoking, and many others are caused by exposure to. Eventually, a tumor forms and the cancer can spread (metastasize) to other areas of the body. Sclc occurs when certain cells in the lungs grow quickly and uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
Some people have a genetic predisposition for lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer grows quickly and in more than half of cases the cancer has spread beyond the lung by the time the condition is diagnosed. From a clinical point of view, we believe the utility of brca2 k3326* genotyping in patients with squamous cell lung cancer should be explored in prospective cohorts.
There are two types of ovarian small cell carcinoma: The two variants of lung cancer that are non small cell (neuroendocrine) in origin are squamous and adenoca of the lung. The majority of lung cancer cases are due to genetic changes known as somatic mutations, which are not hereditary.
This cancer is almost always caused by smoking, but exposure. The majority of lung cancer cases are due to genetic changes known as somatic mutations, which are not hereditary. We don’t know what causes each case of lung cancer.
Each guide is reviewed by experts on the cancer.net editorial board, which is composed of medical, surgical, radiation. Even if they never smoke cigarettes, people with a parent, brother, or sister with lung cancer could have a higher risk of developing lung cancer themselves due to genetic changes. Different factors cause different types of cancer.
About 8% of lung cancers are thought to be inherited or linked to gene changes, but smoking and air pollution remain the primary causes of lung cancer. Or, you can choose another section to learn more about a specific question you have. It is very important to note that having inherited a genetic mutation […]
Because tobacco is a potent carcinogen, secondary causes of lung cancer are often diminished in perceived importance. Furthermore, we investigated the predictive impact of these alterations on the outcomes of modern targeted therapies, their global prognostic significance,. Studies on familial cases of lung cancer have provided evidence for hereditary transmission of lung cancer from one generation to the next generation.
It is typically an aggressive cancer that can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Historically, sclc has been rare in never smokers. The pathogenesis remains unclear, and there are no known predictive or diagnostic biomarkers.
After diagnosis, most people with small cell. The genetic factors that influence small cell lung cancer risk have not received a great deal of attention from scientists, because their impact on cancer susceptibility is overshadowed by the influence of tobacco exposure, says anish thomas, m.b.b.s., m.d., lasker clinical research scholar in ccr’s developmental therapeutics branch. Risk of adenocarcinoma and of small cell lung cancer could be increased by a similar magnitude, although these observations have not been replicated [48, 49].
Historically, sclc has been rare in never smokers. Most lung cancer cases result from smoking or breathing in harmful substances such as radon gas and asbestos but the leading cause of lung cancer may be genetic or hereditary. Almost all affected individuals smoke or have a history of smoking.
However, certain inherited mutations may increase the likelihood of developing sclc. The primary risk factor is tobacco use; A person acquires them during their lifetime.
Evidence suggests that a very small portion of lung cancer cases in the united states, approximately eight percent result from familial risk for lung cancer. But we do know many of the risk factors for these cancers (see lung cancer risk factors) and how some of them cause cells to become cancer. Approximately 8% of lung cancers are inherited or occur as a result of a genetic predisposition (82,87).
Ovarian small cell carcinoma is a rare form of ovarian cancer that typically occurs in young women. To assess the extent of inherited susceptibility to small cell lung cancer (sclc), the most lethal type of lung cancer, we sequenced germline exomes of 87 patients (77 sclc and 10 extrapulmonary small cell) and considered 607 genes, discovering 42 deleterious. Smoking tobacco is by far the leading cause of lung cancer.
Small cell lung cancer commonly leads to paraneoplastic syndromes that affect the endocrine and neurological functions. Cancers begin to develop when genetic mutations affect the genes that control the growth and division of cells or repair dna that is damaged. Inherited predisposition could change small cell lung cancer treatment.
It is characterized by rapid, uncontrolled growth of certain cells in the lungs. In this manuscript, we provided an overview of published studies on sclc’s genomic landscape. Use the menu below to choose the introduction section to get started.
Small cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that almost always affects the lung.