
It is highly active against transitional cell carcinoma; Ad · a forum on the treatment of smoking cessation, focusing on observational studies.
It is not intended, and should not be used as a substitute for the advice of qualified medical professionals.
Intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer. It�s described in intravesical therapy for bladder cancer. Join leading researchers in the field and publish with us. Intravesical chemotherapy may also be used to treat bladder cancer that comes back in the lining of the bladder, especially if intravesical bcg didn’t work.
It is highly active against transitional cell carcinoma; This review will discuss risk stratification of patients with nmibc and role of intravesical therapies in reducing. With nearly 82,000 new diagnoses of bladder cancer projected in the united states in 2020, management of the approximately 75% of patients who present with nonmuscle invasive disease remains challenging.
After instillation, the medication remains in the bladder for a couple of hours. Modalities, ways of administration and indications of these treatments will be. This type of chemo is used for bladder cancer that�s only in the lining of the bladder.
Sodium bicarbonate, which raises the ph of serum and urine, may be used orally or Most people have 1 treatment of intravesical chemotherapy after surgery. Intravesical mitomycin c, epirubicin, and gemcitabine are cytotoxic agents that inhibit dna synthesis in bladder cancer cells.
Superficial bladder cancer is treated by transuretral resection and in some cases by intravesical chemotherapy. It is not intended, and should not be used as a substitute for the advice of qualified medical professionals. Gemcitabine is one of the most common intravesical chemotherapy drugs used to treat bladder cancer.
Epirubicin (pharmorubicin) doxorubicin (adriamycin) gemcitabine (gemzar) The global incidence of bladder cancer is 430,000 patients per year. Intravesical chemotherapy has a critical role in the treatment paradigm of nmibc.
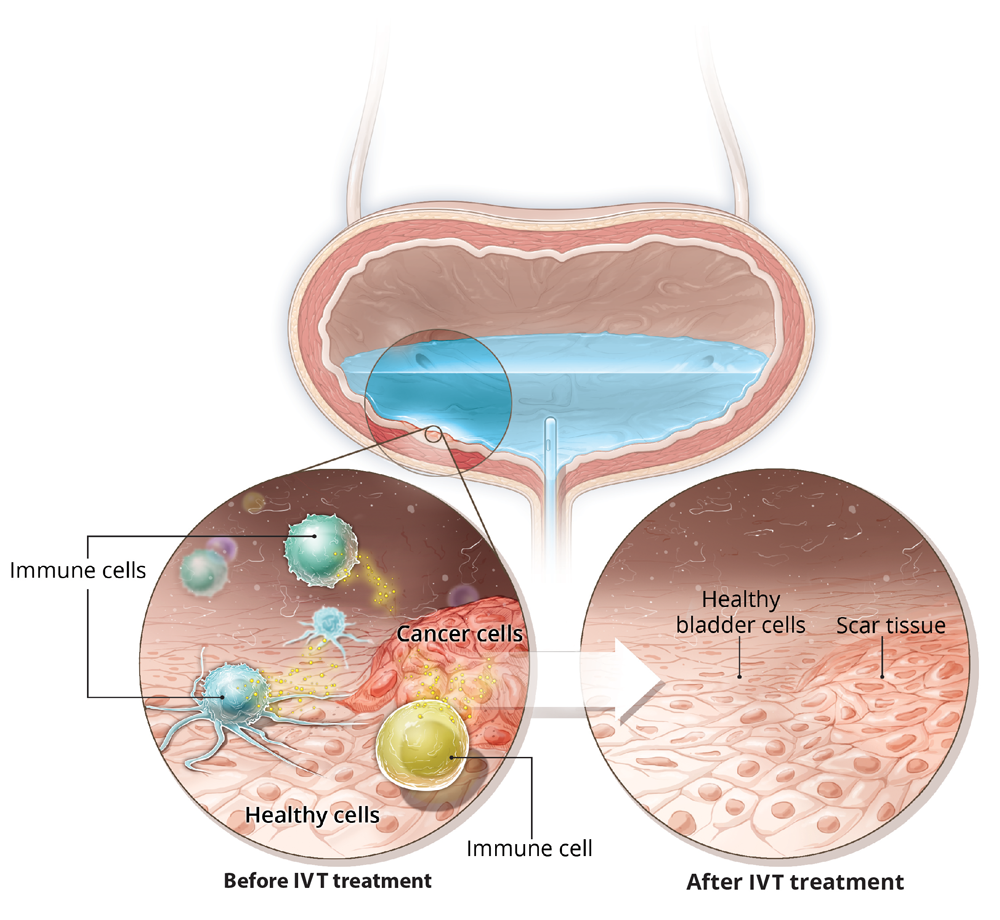
If you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer, intravesical chemotherapy may be recommended as part of your treatment plan. The chemotherapy reduces the risk of the cancer coming back in the bladder lining. However, the biology of the bladder means that intravesical therapy is limited by washout of the agent.
The most common drugs used in intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer are thiotepa and mitomycin. 1 preventing recurrence and progression are important, but intravesical agents expose patients to side effects. Chemo for bladder cancer can be given in 2 different ways:
Intravesical chemotherapy drugs used to treat bladder cancer are: Adjuvant intravesical therapy with either immunotherapy or chemotherapy has been shown to reduce recurrence and/or progression in appropriately selected patients through immunostimulation or direct cell ablation.areas covered: The following are the principal drugs that are used as intravesical chemotherapy or immunotherapy:
At perlmutter cancer center, gemcitabine may be instilled within 24 hours of transurethral resection to help prevent cancer from returning. It helps prevent the cancer coming back (recurrence). The major limitation of hyperthermia as adjunct therapy to cancer management has been the toxicity to normal, unaffected tissue.
This is the most commonly used clinical treatment to prevent recurrence of bladder cancer after surgery [ 11 ]. Ad · a forum on the treatment of smoking cessation, focusing on observational studies. For this treatment, the chemo drug is put right into the bladder.
There has been increased research on hyperthermia and intravesical. Intravesical gemcitabine is the subject of several phase i and ii studies. Per the american urological association.
This type of surgery is called a transurethral resection of a bladder tumour (turbt). After transurethral resection of bladder cancer, intravesical infusion of chemotherapy drugs has a strong killing effect on exfoliated cancer cells, residual cancer tissues, and carcinoma in situ. In bladder cancer, there is increasing evidence that hyperthermia can improve the delivery of intravesical chemotherapy and result in better treatment outcomes.
An intravesical immunotherapy that causes an immune or allergic reaction that has been shown to kill cancer cells on the lining of the bladder. During this procedure, the surgeon removes cancer cells from the lining of the bladder using a small, thin instrument inserted into the bladder through the urethra.