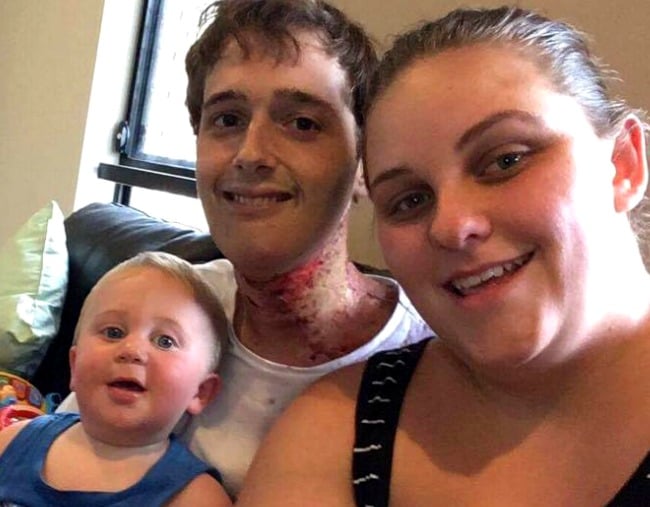

Of these, 26 tumors were tested systematically for hpv as part of the papillomavirus role in oral cancer viral etiology (prove) epidemiological study, which assessed hpv prevalence in sccs across a randomly sampled group of tumors representing all head and neck anatomic subsites. The goal in treatment is to get rid of cancer cells around the.
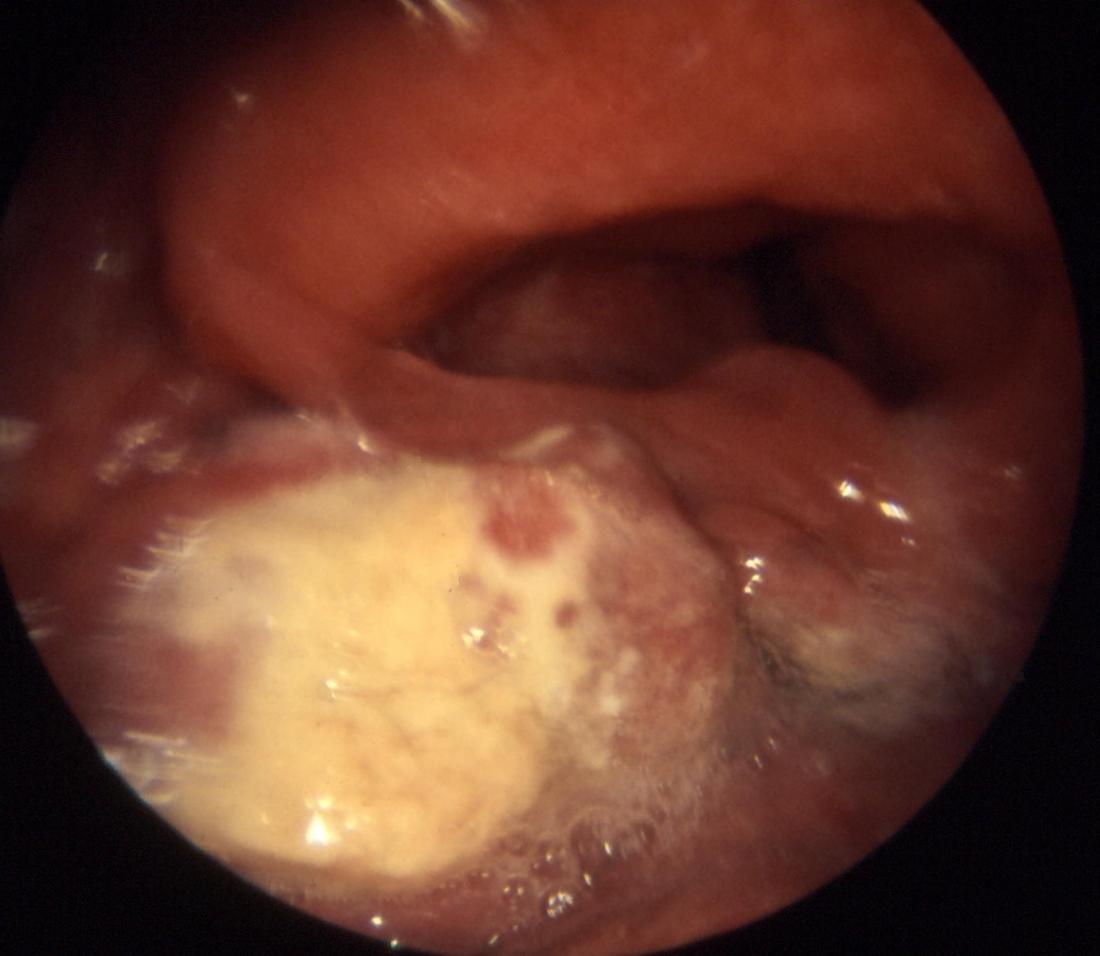
The current treatment landscape for oropharyngeal cancer.
Hpv oral cancer treatment. If signs of cervical cancer are present, treatment options for invasive cancer include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy and patients need to be referred to the right level of services. Treatment for oropharyngeal cancer can include radiation therapy, surgery. 1,303 the hpv cancerwhat is hpv?
Cervical precancer can be treated. Is there a cure for hpv? 2,3 however, approximately 20% of.
It is only when hpv stays in the body for many years, usually decades, that it might cause these oral cancers. Both surgery and radiation work equally well in. However, there are treatments for the health problems that hpv can cause:
The new treatment employs minimally invasive surgery and half the standard dose of radiation therapy, compared to current treatments. However, this approach was not particularly effective at improving how long people lived. Women who get routine pap tests and follow up as needed.
Men are more likely to have oral hpv infection than women. Connection some types of hpv can cause cancer of the tongue, tonsils, throat, cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, and anus. Have a weak immune system ;
Your risk of getting the infection goes up if you: Most patients with stage i or ii oral cavity cancers do well when treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy. The current treatment landscape for oropharyngeal cancer.
These warts are not cancer and are different from other mouth sores but can be a symptom of hpv infection. While human papillomavirus (hpv) is most notable for its involvement in cervical cancer, 1 it should also be understood that hpv is commonly found in the oral cavity as well. A leading cause of a subset of oral cancers, called oropharyngeal cancer, is human papillomavirus (hpv), the same virus that causes cervical cancer.
Most of the time, hpv goes away by itself within two years and does not cause health problems. There is no treatment for the virus itself. Is there any treatment for oral hpv infection?
Learn more about treatment options for oropharyngeal cancer , including targeted therapy and new types of treatment such as immunotherapy being tested in clinical trials. Stages i and ii oral cavity cancer. Oropharyngeal cancer affects the back of the throat, including the base of the tongue and the tonsils.
In a small percentage of cases, the hpv infection may persist, but we do not yet know why this happens. The goal in treatment is to get rid of cancer cells around the. Those tests can be early predictors of hpv caused anal cancers.
Most experts agree that treatment in a clinical trial should be considered for any. In the u.s., a vaccine called gardasil 9 offers almost 100% protection against the strains of hpv associated with types of cancer — specifically, hpv 6,. Chemotherapy (chemo) given along with radiation (called chemoradiation) is another option.
At one time, traditional open surgery was a common treatment for oropharyngeal cancer, often followed by radiation and/or chemotherapy. The vaccine protects against the types of hpv that can cause oropharyngeal cancers, so it may also prevent oropharyngeal cancers. Genital warts can be treated by your healthcare provider or with prescription medication.
No, there are currently no treatments for oral hpv infection. Hpv gets its name from the growth it can cause called a papilloma, or wart. Certain types of hpv are known to cause cancer.
There is some promising evidence for vaccine helping to stop. Most oral infections will be cleared by a healthy immune system without the need for treatment. In the us, nearly 79 million people are infected with hpv.
Human papillomavirus (hpv) is a virus that spreads from having vaginal, anal, or oral sex with a carrier. The virus passes from one person to another during sexual activity. Of these, 26 tumors were tested systematically for hpv as part of the papillomavirus role in oral cancer viral etiology (prove) epidemiological study, which assessed hpv prevalence in sccs across a randomly sampled group of tumors representing all head and neck anatomic subsites.
Can the hpv vaccine prevent oropharyngeal cancers? Oral hpv is thought to spread mainly through oral sex and deep tongue kissing. The hpv vaccine was developed to prevent cervical and other cancers of the reproductive system.
Human papilloma virus (hpv), commonly known as the virus that causes genital warts and cervical cancer in women, is increasingly being recognized now as a cause of infections that colonize the back of the mouth (throat or oropharynx), including the tongue base and tonsils, and potentially a cause of cancer of the head and neck. New technologies have been developed that greatly improve treatment, survival and side effects. The new treatment employs minimally invasive surgery and half.
There is no cure for the virus. If left untreated, genital warts may go away, stay the same, or grow in size or number.