Cervical cancer is caused by sexually acquired infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (hpv). Over 4,000 women die from cervical cancer;
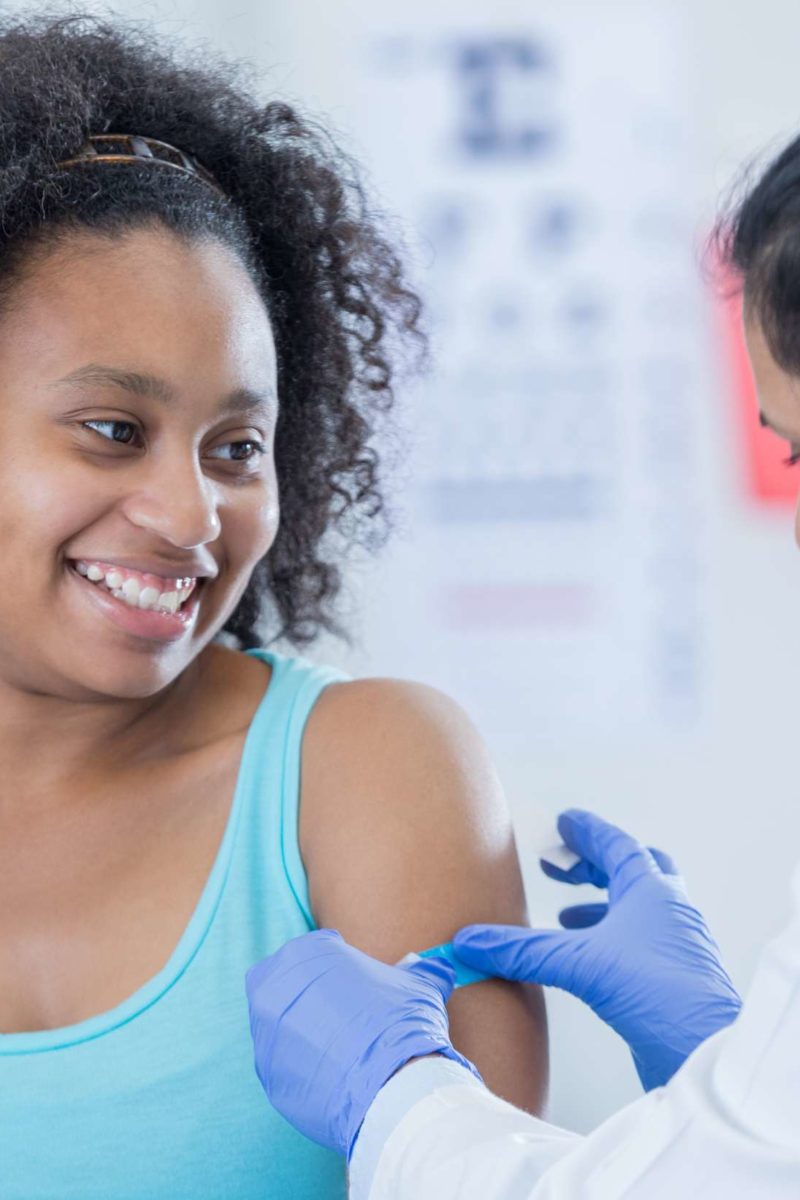
The human papillomavirus (hpv) vaccine is designed to help protect people against the forms of the hpv virus that can lead to cervical cancer.
Hpv leads to cervical cancer. The american cancer society recommends cervical cancer screening with an hpv test alone every 5 years for everyone with a cervix from age 25 until age 65. The primary goal of screening is to identify precancerous lesions caused by hpv so they can be removed. The leading cause of cervical cancer is the human papillomavirus (hpv), which can be exacerbated by smoking cigarettes.
“while cervical cancer is rare, almost 100%. Certain strains of hpv can cause changes in the cells of the cervix, a condition called cervical dysplasia. Worldwide, cervical cancer is one of the most common cancer in women with an estimated 528,000 new cases reported in 2012.
These infections can lead to cervical cancer. Hpv can lead to cervical cancer. The hpv test looks for the infection itself.
Virtually all cervical cancers are caused by hpv. Cervical cancer was once the leading cause of cancer deaths among women in the united states. A new study has found that the hpv vaccine has dramatically lowered cervical cancer rates in the united kingdom since it was introduced in 2008.
If hpv testing alone is not available, people can get screened with an hpv/pap cotest every 5 years or a. Hpv can be detected with very simple tests in which cervical secretions are collected with a swab and tested in a laboratory. Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women globally, with an estimated 570,000 new cases in 2018.
Individuals infected with both hpv and hiv have an increased risk of developing cervical or anal cancer. Hpv vaccines and cervical cancer screening have made it one of the most preventable cancers. What does the science say?
Cervical cancer develops in a woman�s cervix (the entrance to the uterus from the vagina). The study followed nearly 1.7 million girls and women ages 10 through 30. Vaccination according to the cdc, hpv is most common in individuals who are in their late teens and early 20s.
Cervical cancer was diagnosed in 19 women who had received the hpv vaccine, and in 538 women who had not received it, leading researchers to conclude the vaccine is associated with a substantially reduced risk of invasive cervical cancer. Cervical cancer is seen in a woman�s cervix (which is the entrance to the uterus from the vagina). It is one of the most common types of cancer that women suffer.
The hpv test or the pap test can. Over 4,000 women die from cervical cancer; Prospective studies have shown that 15 to 28% of women in whom hpv dna was detected developed sil within 2 years, compared to only 1 to 3% of women in whom hpv dna was not detected.
Early warning signs of cervical cancer include abnormal discharge, bleeding after sex, and bleeding between periods. Screenings should begin as early as age 21. The human papillomavirus (hpv) vaccine is designed to help protect people against the forms of the hpv virus that can lead to cervical cancer.
However, just because a woman has hpv or cervical dysplasia does not necessarily mean she will get. Most hpv infections clear spontaneously but. Hpv type 16 is the strain most likely to cause cancer and is present in about 47% of all cervical cancers, and in many vaginal and vulvar cancers, penile cancers, anal cancers, and cancers of the head and neck.
How is hpv related to cervical cancer? Hpv can cause cervical, vaginal, vulvar, and other cancers in women, as well as common and genital warts. Smoking can also raise the risk of cervical cancer in women with hpv.
The pap test looks for changes in cervical cells caused by hpv infection. Hpv causes nearly all cervical cancers. Even women who are vaccinated should still get regular cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer can be found early and even prevented with routine screening tests. Before we explore the link between cervical cancer and smoking, let’s look at why smoking tobacco is harmful to your health. Hpv infections are also implicated in the development of other types of carcinomas.
Hpv is almost always the cause of cervical cancer. If it is not treated, dysplasia can advance to cervical cancer. Cervical cancer is caused by sexually acquired infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (hpv).
The key to preventing hpv infection is vaccination. These may eventually develop into cancer if they’re not found and removed in time. There is also evidence linking hpv with cancers of the anus, vulva, vagina, penis and oropharynx.
Human papillomaviruses (hpv) have two proteins known as e6 and e7 which turn off some tumor suppressor genes, such as p53 and rb. Cervical cancer is the most common cancer linked to hpv in people with a cervix. The hpv immunisation programme has successfully almost eliminated cervical cancer in women born since sept 1,.
Some cervical cancers come from hpv infection of gland cells in the cervix and are called adenocarcinomas. But hpv is not the only cause of cervical cancer. This may allow the cells lining the cervix to grow too much and to develop changes in additional genes, which in some cases can lead to cancer.
Chronic or persistent infection of hpv is essential but hpv alone is inadequate, additional endogenous. Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by hpv. Hpv infections and cervical cancer.
However, most genital hpv infections will not cause cancer. Hpv can cause cancer of the mouth and tongue. Routine screening can prevent most cervical cancers by allowing health care providers to find and remove precancerous cells before they develop into cancer.
For women, getting regular pap smears reduces the risk of developing cervical cancer. 11,000 women are diagnosed with cervical cancer caused by hpv;