
Rates of one type of head and neck cancer affecting the area of the throat behind the mouth, the oropharynx, have dramatically risen in recent years, driven by hpv, which now accounts for roughly 75 percent of all cases of oropharyngeal. Tobacco and alcohol use have been reported to be associated with hnscc.
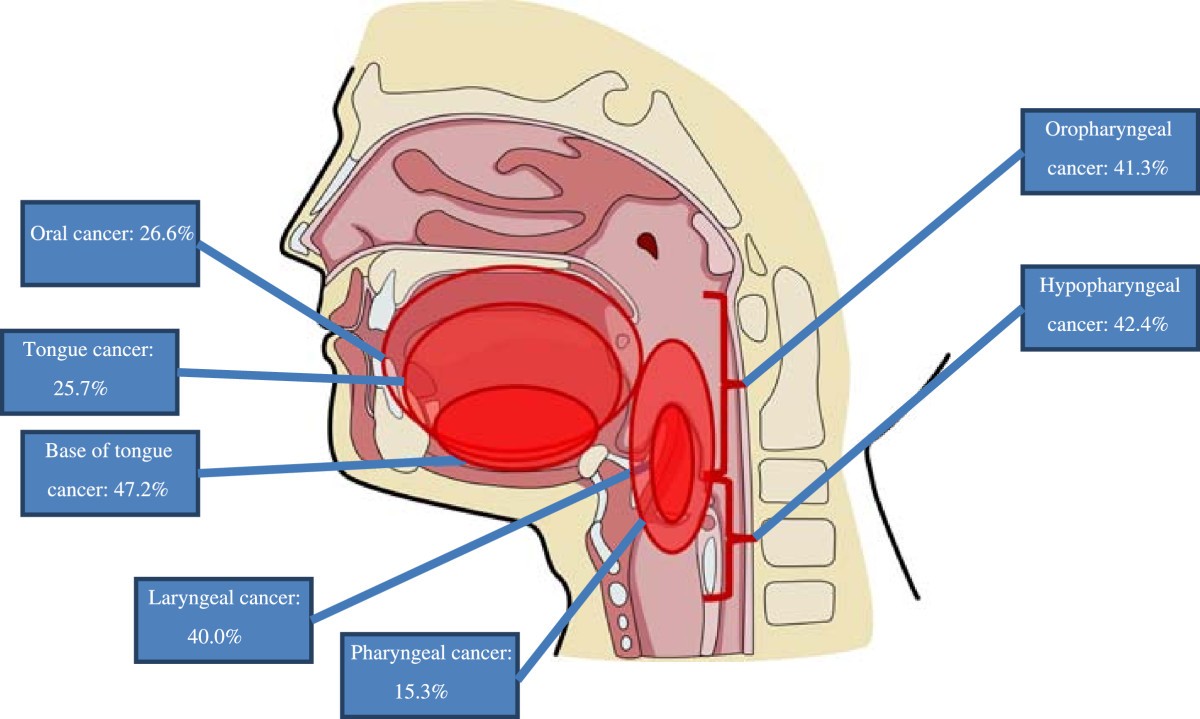
Head and neck cancer is a common cancer in the united states and worldwide, especially in adults aged 50 years and older.
Hpv and head and neck cancers. The “high risk” hpv subtypes most clearly implicated in cancer are hpv16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 51, 52, and 56, which are capable of causing cancers of the cervix, head and neck, anus, vagina, vulva, and penis [6]. Prevalence was significantly higher (36%) in oropharyngeal cancer, and could exceed 50%, especially in tonsillar. Just as hpv is the main cause of cervical cancers, it also causes cancers that grow in the back of the throat.
Exposure to typical carcinogens and infection of human papillomavirus (hpv). The most common forms of head and neck cancer today are those related to the human papilloma virus (hpv). Rates of one type of head and neck cancer affecting the area of the throat behind the mouth, the oropharynx, have dramatically risen in recent years, driven by hpv, which now accounts for roughly 75 percent of all cases of oropharyngeal.
We don’t know for sure how hpv causes head and neck cancer. Two vaccines are currently available for the prevention of hpv infection. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (hnscc) is a unique malignancy associated with two distinct risk factors:
3 today, research shows that hpv is the main cause of cervical cancer. There are many types of hpv. Most head and neck cancers caused by hpv are in the throat, in the base of the tongue and the tonsils.
Over 20 million americans have some type of genital or oral hpv infection. In a new study, researchers have confirmed that infection with human papillomavirus (hpv) 16 precedes the development of some head and neck cancers. This book reflects the multidisciplinary nature of the scientific and clinical questions involved in this disease.
However, many members of the general public and even members of the medical community aren�t aware of the strong link between hpv and head and neck cancers. The most commonly implicated subtype in hnscc is hpv16, accounting for over 80% of hpv+ hnscc [14,15]. And there are two major subtypes that you may have heard about in the media and that�s hpv positive and hpv negative.
Hpv is a sexually transmitted infection that can infect the oropharynx (tonsils and back of throat), anus, and genitals. Hpv can cause cancer, warts or have no effect. Increasingly, these infections are including those of the mouth and throat—signaling that hpv is a growing risk factor for developing head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer is a common cancer in the united states and worldwide, especially in adults aged 50 years and older. Head and neck cancer is a common cancer in the united states and worldwide, especially in adults aged 50 years and older. What is human papillomavirus (hpv)?
A causal relationship between cervical cancer and a sexually transmitted source was first hypothesized in 1842. As human papillomavirus (hpv) causes a rising number of oropharyngeal cancers, understanding the biological, clinical and social implications of this infection has become increasingly important for head and neck practitioners. Hpv lives in mucous membranes and can be passed by genital contact in vaginal, anal and oral sex.
However, some people aren’t able to get rid of their hpv infection. We can’t predict whose infection will disappear and who will develop cancer. They are now using this technique to analyse tissue samples taken from patients to gain a better understanding of how hpv causes head and neck cancer.
Hpv is not known to cause other head and neck cancers, including those in the mouth, larynx, lip, nose, or salivary glands. Most head and neck squamous cell carcinomas of the mouth and voice box are caused by tobacco and alcohol use ( 8 ). Patient risk profiles for opc and oral cavity cancer differ.
Hpv is very common in the u.s. The new study is the first to do so using samples collected from. Our scientists have been developing a new screening method that detects human papillomavirus (hpv) in the mouth.
Hpv is a small dna virus that is capable of infecting human keratinocytes of the skin and mucous membranes. So the most common type of head and neck cancer, the one we see most frequently in our clinic, is called head neck squamous cell carcinoma, which encompasses the vast majority of different diagnoses. Doctors have long known that the human papilloma virus (hpv) is linked to cervical cancer.
4 hpv is also linked with the risk of developing head and neck cancer (hnc), specifically opc. Tobacco and alcohol use have been reported to be associated with hnscc. Hpv encodes the potent oncoproteins e6 and e7, which bypass many important oncogenic processes and result in cancer development.
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (hnsccs) arise in the mucosal lining of the upper aerodigestive tract. What are the symptoms of oropharyngeal cancer? Uncovering the link between hpv and head and neck cancer.