How is prostate cancer detected? In 2018, there were 1,276,106 new cases and 358,989 deaths.

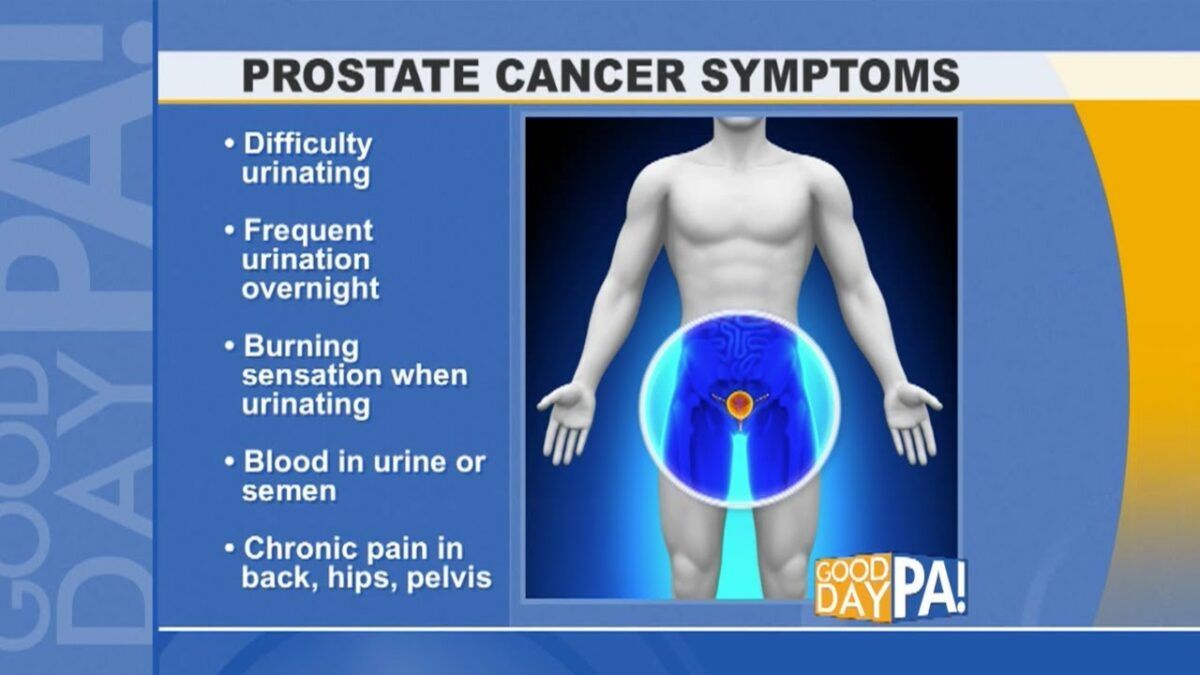
Problems urinating, including a slow or weak urinary stream or the need to urinate more often, especially at night;
Detection of prostate cancer. The psa test measures the level of psa in your blood. Problems urinating, including a slow or weak urinary stream or the need to urinate more often, especially at night; This is an example of a prostate cancer care that would include pet scanning.
Ensemble learning can detect 96.55%of true positive prostate cancer in our model. It does not specifically test for cancer. Prostate cancer (pca) is the second most frequent type of cancer found in men worldwide and the fifth leading cause of death by cancer.
We studied whether this improves the detection of prostate cancer. The sensitivity of prostatic biopsy is about 50%. Noninvasive tests that can accurately detect prostate cancer are urgently needed for prostate cancer diagnosis, surveillance and prognosis.
Finding a small tumor, however, may not necessarily reduce a man’s chance of dying from prostate cancer. The fusion of magnetic resonance imaging (mri) data with trus enables the targeted biopsy of suspicious areas. These initiatives have yielded several novel pca biomarkers, including the phi, a biomarker that has received the approval of the us food and drug administration (fda) for prostate cancer detection.
Elevated psa levels may indicate cancer, but the majority of men with an elevated psa dont actually have prostate cancer. Yet, changes in psa threshold, frequency of screening, and addition of other biomarkers have potential to minimise overdiagnosis associated with psa screening. Prostate mri radiomics and blood kallikreins have been proposed as tools to improve the performance of biparametric mri (bpmri).
Psa in the blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml). Psa is a protein produced by the cells of the prostate. There is no single test to detect prostate cancer.
Therefore, this document focuses only on the efficacy of psa screening for the early detection of prostate cancer with the specific intent to reduce prostate cancer mortality and not secondary tests often used after screening to determine the need for a prostate biopsy or a repeat prostate biopsy (e.g., psa isoforms, pca3, imaging). Prostate cancer is confirmed by a core needle biopsy with imaging either before or during the procedure. After a cancer diagnosis, staging provides important information about the extent of cancer in the body and anticipated response to treatment.
Prostate cancer is detected by the results of screening psa with a blood test or a dre. Signs and symptoms of prostate cancer. The current available systematic prostate biopsy is performed only under ultrasound guidance, but new imaging techniques allow prostate cancer visualization and therefore improved detection.
Many doctors use a psa cutoff point of 4 ng/ml or higher when deciding if a man might need further testing, while others might. The psa level in blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml). Most prostate cancers are found early, through screening.
Exfoliated prostate cells captured in urine represent a promising resource for noninvasive detection of prostate cancer. So it�s great news that a new programme to detect prostate cancer is likely to become part of the nhs armoury within three to five years. In 2018, there were 1,276,106 new cases and 358,989 deaths.
Accurate detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (cspca), gleason grade group ≥ 2, remains a challenge. The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the psa level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesn’t have prostate cancer. A better way to detect prostate cancer.
More advanced prostate cancers can sometimes cause symptoms, such as: 168 men with suspected prostate cancer underwent prostate mri after a previous negative biopsy. A team from the chum research centre (crchum) and polytechnique montréal combines raman microspectroscopic imaging with machine learning techniques to better detect aggressive forms of prostate cancer, making diagnosis accurate almost 9 times out of 10.
The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the psa level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesn’t have prostate cancer. How is prostate cancer detected? Among the six machine learning techniques, logistic regression, neuralnetworks, and ensemble learning have the potential to reach an accuracy of 95.00 percent.
Blood in the urine or semen Early detection of prostate cancer by psa screening remains controversial; When used in screening, the psa test can help detect small tumors that do not cause symptoms.
The two most common tests are the prostate specific antigen (psa) blood test and the digital rectal examination (dre). Many doctors use a psa cutoff point of 4 ng/ml or higher when deciding if a man might need further testing, while others might. Virtually all psa is produced by the prostate gland.
Several new biomarkers appear promising in individuals with elevated psa levels or those diagnosed with. This year, 4,200 canadian men will die of prostate. Detecting prostate cancer early may not reduce the chance of dying from prostate cancer.
Early prostate cancer usually causes no symptoms. Moving on from the standard psa blood test, which can give.