Chung, md, gastroenterology division, center for cancer risk assessment, massachusetts general hospital, harvard medical school, grj 704, 50 blossom street, boston, massachusetts 02114. Early detection of crc leads to improvement in cancer survival rate.
1 although crc incidence and mortality have declined overall as a result of an increased uptake of screening, 2 work remains to be done since 40% of eligible individuals are not compliant with crc.
Colorectal cancer genetic testing. Our clinical genetics service offers counseling and education about the risk of hereditary forms of colon cancer, as well as genetic testing for you and your family members. Genetic testing genetic testing is available for some families with features of a genetic predisposition. Colorectal cancer (crc) is among the most prevalent and preventable forms of cancer worldwide, accounting for over 600,000 deaths in 2005.
The only way to know if you have hereditary colorectal cancer is through genetic testing. Genetic testing will not identify the cause for some hereditary colorectal cancers, because the genes affected in these cancers are not yet known. Your healthcare provider will rub the swab between your cheek and gums to collect the sample.
Genetype for colorectal cancer is a dna test from a cheek swab. What is colon cancer genetic testing? Surgery is often the most effective way to treat or prevent bowel cancer.
1 approximately 20% to 30% of crcs are potentially linked to genetic factors, and hereditary crc. Hindawi�s academic journals cover a wide range of disciplines. 70+ genetic markers of colorectal cancer risk;
Diagnosed with colon cancer or rectal cancer under age 50 During genetic testing, we may take a sample of tissue from your blood, a polyp, or a tumor (if you already have colon cancer). We’ll look at the sample for changes in your genes that are associated with.
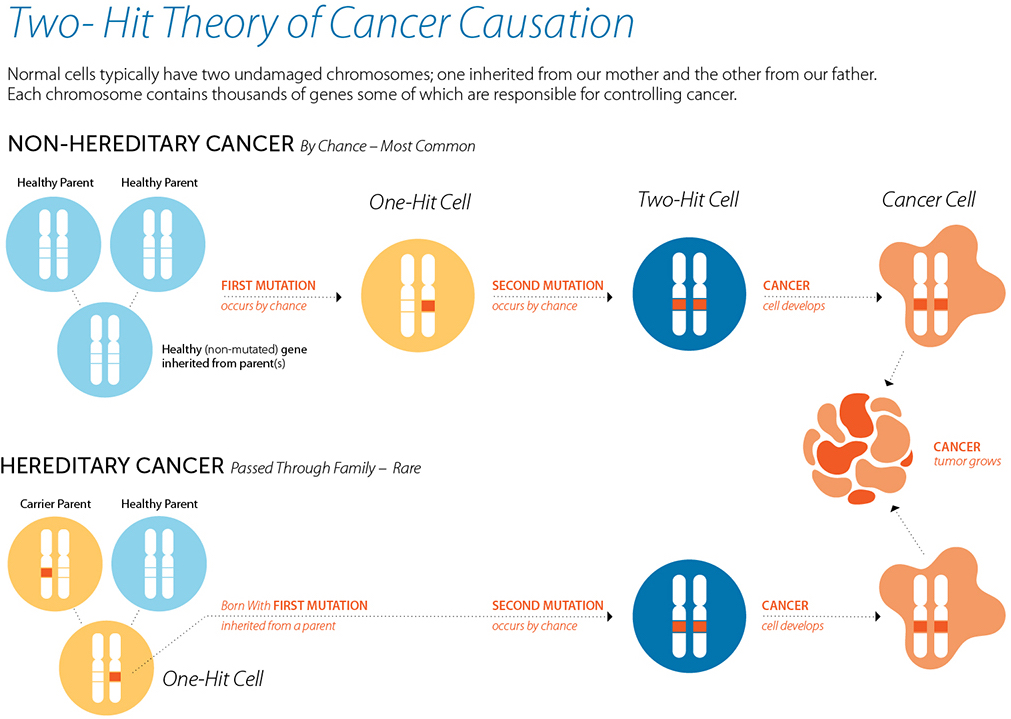
Genetic testing raises clinical, ethical, legal, and psychosocial questions that must urgently be discussed. This checks for bowel cancer or polyps that may develop into bowel cancer. Up to 30% of these cases exhibit familial clustering, which means that tens of thousands of individuals have a disease with a potentially definable genetic componen.
Anyone who meets the following criteria is a candidate for genetic testing. Integrated risk score that accounts for: A technical standard of the american college of medical genetics and genomics (acmg) genet med.
Genetic testing for inherited colorectal cancer and polyposis, 2021 revision: Who, when, how and why. It could mean a somewhat higher risk for colon cancer, and earlier, more frequent colonoscopies.
Colorectal cancer (crc) is the fourth most frequently diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death in the united states; Usually, genetic testing will be recommended if your tumor screening results (ihc or msi) are abnormal Chung, md, gastroenterology division, center for cancer risk assessment, massachusetts general hospital, harvard medical school, grj 704, 50 blossom street, boston, massachusetts 02114.
Early detection of crc leads to improvement in cancer survival rate. 4, 5 crc in lynch syndrome has unique histopathologic and clinical. If appropriate, we will discuss this with you.
Genetic testing for inherited colorectal cancer and polyposis, 2021 revision: Colon and gynecologic cancer screening rates have been shown to increase or be maintained among carriers of mmr pathogenic variants within the year after disclosure of results, while screening rates decrease among noncarriers. Your genetics specialist will explain whether you need this test, when you should start having it and how often.
Reprint requests address requests for reprints to: Genetic testing in colorectal cancer: Genetype for colorectal cancer is the only test that combines the following to give you a comprehensive and highly accurate risk prediction score 4.
Genetic testing for colon cancer. Colon cancer genetic testing is a blood test that can tell you whether you carry rare changed, or mutated, genes that can cause colon cancer. Colon cancer remains the third leading cause of death due to cancer in the us, where it affected more than 145,000 individuals in 2005.
Colorectal cancer (crc) is the third most common cancer in the united states, diagnosed at a median age of 69 years for men and 72 years for women. However, other studies have demonstrated the possibility of increased distress following genetic testing for fap. Although most people who get colon cancer do not have one of these mutated genes, having them greatly increases your chance of getting colon cancer.
Genetic testing and early onset colon cancer. A technical standard of the american college of medical genetics and genomics (acmg) download pdf acmg technical. Both genetic and environmental factors contribute to cancer etiology and estimates suggest that at least one third of crc has a familial component.
Your family history of colorectal cancer (if any) your personal history Your doctor may talk to you about having surgery to remove an area of bowel if a colonoscopy finds changes that are. In 2019, an estimated 101,420 new cases of colon cancer and 44,180 new cases of rectal cancer will be diagnosed.
Colorectal cancer (crc) is the second leading cause of cancer related death in the world after lung cancer. The colorectal cancer comprehensive panel examines 22 genes associated with an increased risk for hereditary colorectal cancer (colon cancer). Early detection could facilitate the initiation of targeted prevention strategies and surveillance for crc patients and their families.
There is no evidence yet that this test can reduce deaths from colorectal cancer. 1 although crc incidence and mortality have declined overall as a result of an increased uptake of screening, 2 work remains to be done since 40% of eligible individuals are not compliant with crc. A blood test for an altered gene called sept9 is fda approved to be used to screen adults 50 years or older at average risk for colorectal cancer who have been offered and have a history of not completing colorectal cancer screening.
Environmental factors may increase the chance of developing bowel cancer high intake of red and processed meat can increase the chance of developing bowel cancer, Genetic testing can identify genes that cause these syndromes.