From 2013 to 2017, incidence rates dropped by about 1% each year. When found early, most bowel cancer cases can be successfully treated.
The exam might not detect all small polyps and cancers.
Colon cancer screening frequency. 3 years • ssp ≥ 10 mm: Colorectal cancer colorectal cancer screening options test frequency advantages disadvantages fobt annual inexpensive/noninvasive; When found early, most bowel cancer cases can be successfully treated.
Several test options are available for colorectal cancer screening: • ≤ 20 hps in rectum or sigmoid colon < 10 mm: Start colon cancer screening at age 45 by the type of screening test that would work best for you;
Visual exams* include a colonoscopy every 10 years, ct (virtual) colonography every 5 years, and a flexible sigmoidoscopy (fsig) every 5 years. Continue with regular colon cancer screening until age 75 as long as you are healthy ; The exam might not detect all small polyps and cancers.
Test options for colorectal cancer screening. In the united states, colorectal cancer is most common in adults aged 65 to 74. 75% of colorectal cancer occurs in people with no known risk factors.
3 years • ssp with dysplasia: The gold standard for screening, a colonoscopy, only needs to be done once every 10 years for people at. If you�re between 60 and 74 years, you�ll automatically be invited to use a home testing kit for an fob test every two years.
2 it is estimated that 10.5% of new colorectal cancer cases occur in persons younger than 50 years. 45,230 new cases of rectal cancer. Colonoscopy is one of the most sensitive tests currently available for colon cancer screening.
6 the uspstf commissioned a systematic review to evaluate the available evidence for colorectal cancer screening and found 33 studies including 10,776,276 patients. 10 years • ≤20 hps proximal to sigmoid colon: Every 10 years (for people who do not have an increased risk of colorectal cancer).
1 colorectal cancer is most frequently diagnosed among persons aged 65 to 74 years. Mortality associated with colorectal cancer can be reduced by early detection. Repeated testing needed to achieve adequate sensitivity fecal
Colonoscopy may be repeated in 10 years if distal, small (less than 10 mm) hyperplastic polyps are the. Colorectal cancer is the third leading cause of cancer death for both men and women, with an estimated 52,980 persons in the us projected to die of colorectal cancer in 2021. When detected early, colorectal cancer is one.
Immunochemical tests are accurate and do not require dietary or medication changes before testing. More than 10 synchronous adenomas warrant surveillance colonoscopy in less than three years. Highly sensitive fecal immunochemical test (fit) every year;
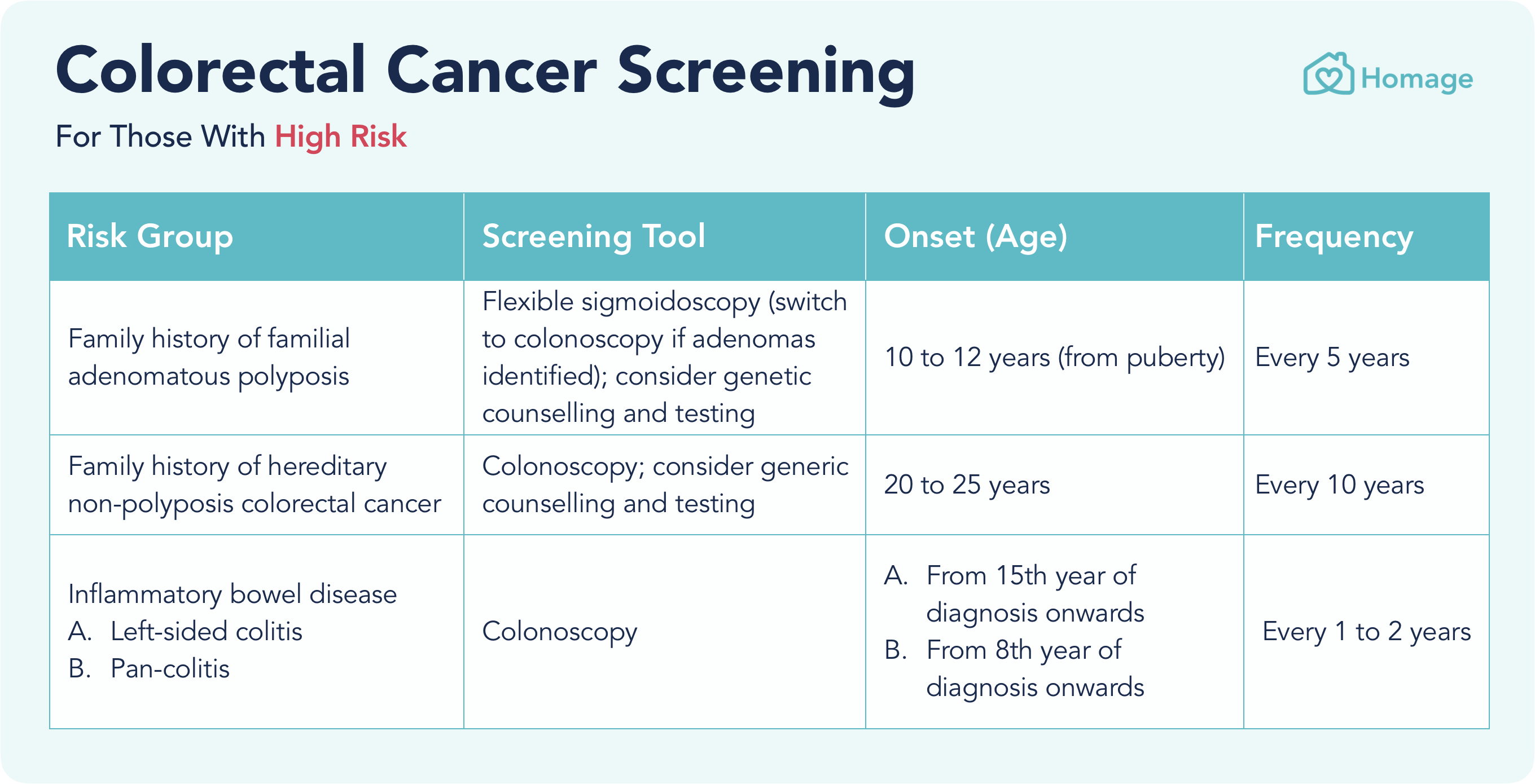
*if a person chooses to be screened with a test other than colonoscopy, any abnormal test result should be followed up with colonoscopy. People with a family history of hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer colonoscopy every one to two years, starting at age 20 to 25 or2 to 5 years before. We examined the frequency of colorectal cancer screening in 4 canadian provinces and the influence of patient contact with a family physician on the uptake of cancer screening.
The doctor can view your entire colon and rectum. Ad 90% of people diagnosed with colon cancer are over age 50. From 2013 to 2017, incidence rates dropped by about 1% each year.
The nhs bowel cancer screening programme in england is offered to people aged 55 or over, as there is a higher risk of bowel cancer with increasing age: However, the participation of eligible people in colorectal cancer screening is thought to be inadequate. Test age at initial screening frequency fecal immunochemical test (fit) 45 years annually through age 75 colonoscopy 45 years every 10 years through age 75
Abnormal tissue, such as polyps, and tissue samples (biopsies) can be removed through the scope during the exam. National bowel cancer screening program. Screening colonoscopies (hcpcs g0105) may be paid when performed by a doctor of medicine or osteopathy at a frequency of once every 24 months for beneficiaries at high risk for developing colorectal cancer (i.e., at least 23 months have passed following the month in which the last covered hcpcs g0105 screening colonoscopy was performed).
Starting at age 45, individuals with an average risk of colorectal cancer should undergo regular screening with one of six different tests, depending on patient preference and test availability. And screening is one of the most effective ways to detect early signs of bowel cancer.