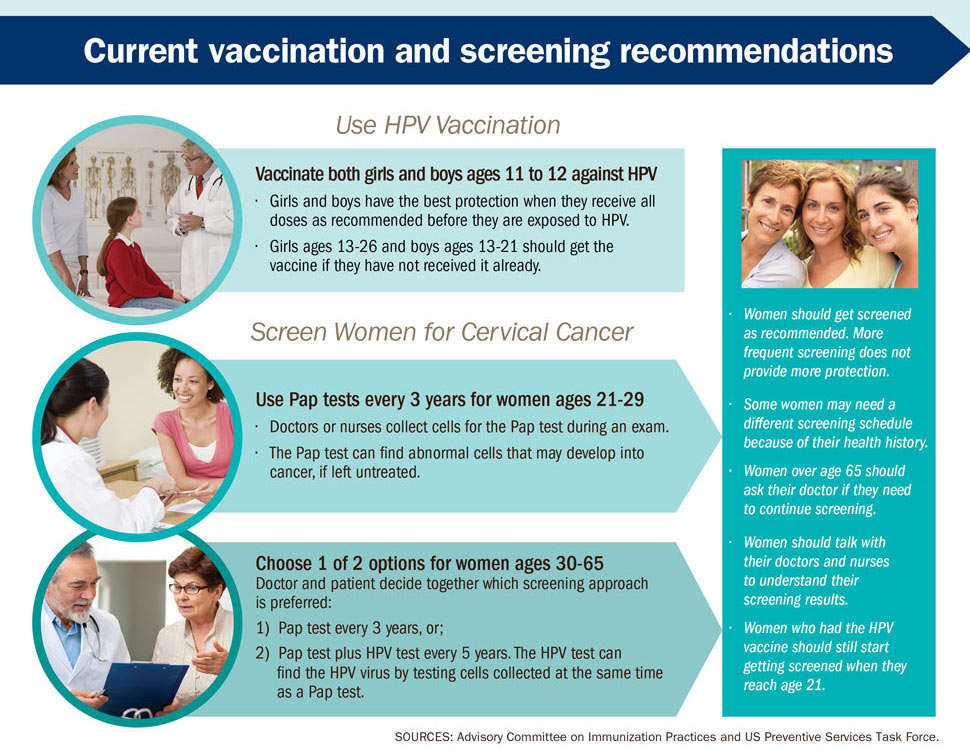
In most cases cervical cancer can be prevented. The human papillomavirus (hpv) vaccine is designed to help protect people against the forms of the hpv virus that can lead to cervical cancer.
Hpv infections and cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer from hpv. There are many types of hpv. But sometimes the virus leads to cancer. It’s important both males and females receive all doses of the hpv vaccine.
Unlike many cancers, it is primarily a disease of the young; Widespread immunization with the hpv vaccine could reduce the impact of cervical cancer and other cancers caused by hpv worldwide. Human papillomavirus infection (hpv) causes more than 90% of cases;
An overview of quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine safety: It is one of the most common types of cancer that women suffer. Individuals infected with both hpv and hiv have an increased risk of developing cervical or anal cancer.
The majority of people with a cervix who experience an hpv infection will not develop cervical cancer, but regular screening is very important. A new study has found that the hpv vaccine has dramatically lowered cervical cancer rates in the united kingdom since it was introduced in 2008. We sought to estimate the effect of hpv vaccination on cervical cancer incidence from observed data.
Cervical cancer is caused by a virus called hpv. Cervical cancer is seen in a woman�s cervix (which is the entrance to the uterus from the vagina). You can get hpv from:
The main signs of cervical cancer are: Most women�s bodies are able to fight hpv infection. Though usually harmless, some types of hpv cause cervical lesions that, over a period of time, can develop into cancer if untreated.
Since then, the link between hpv and cervical squamous cell carcinoma has become well established. The virus spreads through sexual contact. Cervical cancer is a cancer that�s found anywhere in the cervix.
Worldwide, cervical cancer is one of the most common cancer in women with an estimated 528,000 new cases reported in 2012. It grows very slowly and how serious it is depends on how big it is. Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by an infection from certain types of human papillomavirus (hpv).
Most people who have had hpv infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. Most hpv infections clear spontaneously but. Routine screening can prevent most cervical cancers by allowing health care.
The most common cause of cervical cancer is the human papillomavirus (hpv), and dr. For a patient at the doctor’s office, an hpv test and a pap test are done the same way—by collecting a sample of cervical cells with a scraper or brush. Published reports on the effect of hpv vaccination on incidence of invasive cervical cancer have been scarce.
In most cases cervical cancer can be prevented. Hpv infections and cervical cancer. In 2012, cervical cancer was responsible for 266,000 deaths worldwide.
Turaka says receiving the hpv vaccine is the best way to prevent cervical cancer. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus, the place where a baby grows during pregnancy. Almost all cervical cancers are caused by human papillomavirus (hpv), a common virus that can be passed from one person to another during sex.
Hpv is also responsible for other diseases such as recurrent juvenile respiratory papillomatosis (a disease in which tumours grow in the air passages leading from the nose and. An hpv test looks for the human papillomavirus, a virus that can cause cervical cancer. [3] [14] other risk factors include smoking , a weak immune system , birth control pills , starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important.
Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by an infection from certain types of human papillomavirus (hpv). Some hpv types can cause changes on a woman’s cervix that can lead to cervical cancer over time, while other types can cause genital or skin warts. Vaginal, anal or oral sex;
You�re at higher risk if you smoke, have had many children, use birth. For an hpv/pap cotest, an hpv test and a pap test are done together. By improving awareness of the general population on cervical cancer prevention, by providing tools to health care providers to better address vaccine misinformation, by alleviating fears on vaccine safety, by making hpv vaccines more affordable and accessible, and by reinforcing messaging to empower and remind parents of the importance of hpv.
The other types of cancer caused by hpv may not be detected until they cause more serious health problems. The nhs says that it can often be prevents by screening which can treat abnormalities before they turn into cancer. It�s part of the reproductive system and is sometimes called the neck of the womb.
A 2014 study done in nepal found that knowledge and awareness of hpv, cervical cancer, and the vaccine were low among women in two villages in that country, but that acceptance of a “freely available hpv vaccine for children was high, indicating potentially high uptake rates in these communities,” the researchers wrote in the asian pacific. Cervical cancer is caused by sexually acquired infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (hpv). Hpv can lead to cervical cancer.
The human papillomavirus (hpv) vaccine is designed to help protect people against the forms of the hpv virus that can lead to cervical cancer. Anyone with a cervix can get cervical cancer. The link between genital hpv infections and cervical cancer was first demonstrated in the early 1980s by harold zur hausen, a german virologist.
The cervix is the opening between the vagina and the womb (uterus). Who is more likely to get cervical cancer. Most cervical cancers are associated with human papillomavirus (hpv), a sexually transmitted infection.
Virtually all cervical cancers are caused by hpv. Half of all cases are diagnosed before the age of 47, with a. Cervical cancer is the only type of cancer caused by hpv that can be detected early by a recommended screening test.
It is the third most common cancer worldwide, and the 12 th most common in the uk. Some cervical cancers come from hpv infection of gland cells in the cervix and are called adenocarcinomas. Cervical cancer develops in a woman�s cervix (the entrance to the uterus from the vagina).
Hpv type 16 is the strain most likely to cause cancer and is present in about 47% of all cervical cancers, and in many vaginal and vulvar cancers, penile cancers, anal cancers, and cancers of the head and neck.