If the cancer is at a very early stage, such as stage ia, most doctors believe it is safe to continue the pregnancy to term and have treatment several weeks after birth. A simple hysterectomy to remove the uterus and cervix may be used to treat severe cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (abnormal cervical cells), some early cervical cancers or invasive cervical cancer.
There are different types of hysterectomy:
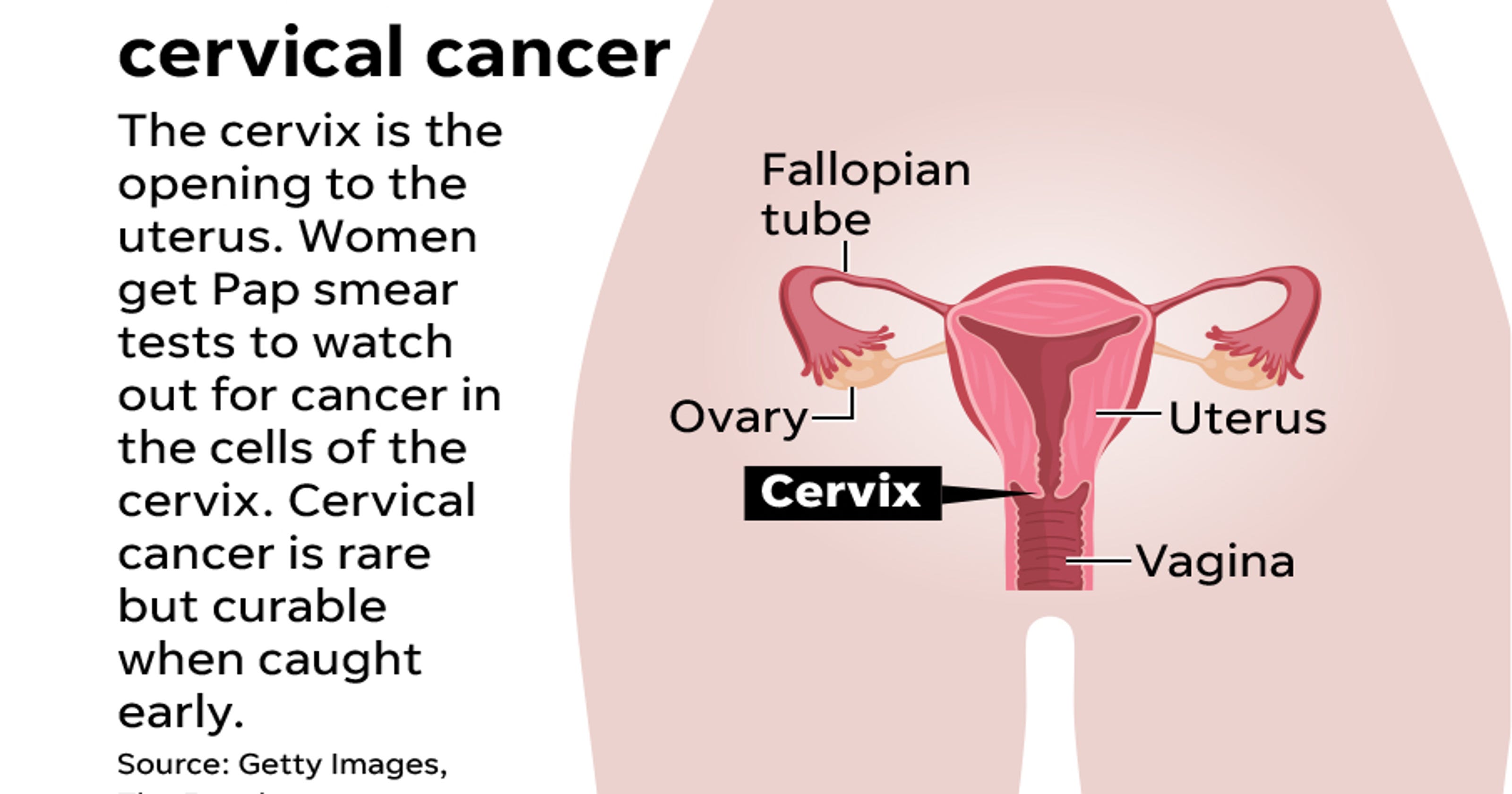
Cervical cancer and hysterectomy. Depending on the woman’s age and the type of cancer, removal of the ovaries & fallopian tubes may also be recommended. It is not certain if this improves survival. A hysterectomy is surgery to remove some or all of a woman’s reproductive organs.
If you have had a hysterectomy in which your cervix was removed and: No problems never diagnosed with cancer just precancer. There are different types of hysterectomy:
4,5 in 1992, the laparoscopic approach for radical hysterectomy to treat. The specific type of cervical cancer; It involves removing the uterus, and in the case of cervical cancer, the cervix.
Hysterectomy is a common part of cervical cancer treatment. •after total hysterectomy if no cin2/3 or cervical cancer •if cin2+ and cervix removed, after initial post treatment surveillance, continue screening of vaginal cuff with cytology every 3 years for 20 years, even if >65 •screening should not resume for any reason The cervix is the tube of tissue that connects the bottom of the uterus, also known as the womb, with the vagina.
That includes stage i cervical cancer, and more specifically, stage ia2 and ib1. A hysterectomy involves removing the womb and cervix, and occasionally the fallopian tubes and ovaries. 9 years ago my gynecologist tested and said zero stage cancer in situ i opted to have everything removed.
Typically, these patients receive radiation and chemotherapy. The advantages of a simple hysterectomy include: If you have stage 1a1 cervical cancer, a hysterectomy may be an option.
Hi just wanted to share my story. Hysterectomy is the usual treatment for early stage cervical cancer. If you had a hysterectomy as a treatment for cancer, you should know that your cancer can still come back.
The advantages over abdominal radical hysterectomy (arh) include shorter operating times, less blood loss, lower transfusion rates, and a shorter hospital stay. Cervical cancer is cancer that grows in cells from a woman’s cervix. On the other hand, if a radical hysterectomy was done because of cervix cancer, recurrence rate may be up to 9%.
People who have had a full hysterectomy are less likely to develop cervical cancer. Yet sometimes cancerous cells remain behind at the edges of the extracted tissue. A simple hysterectomy to remove the uterus and cervix may be used to treat severe cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (abnormal cervical cells), some early cervical cancers or invasive cervical cancer.
This may be done with an abdominal hysterectomy, a vaginal hysterectomy, a laparoscopic hysterectomy (in. A doctor may also remove a. When the entire uterus is removed — cervix included.
In many patients, the pelvic and abdominal lymph nodes, ovaries and fallopian. What are the advantages of a simple hysterectomy? A radical hysterectomy is the removal of the womb, cervix, tissue around the cervix.
A hysterectomy is a type of surgery that remove the womb (uterus) and cervix. Simple hysterectomy (also called a total hysterectomy). An analysis of the national cancer database (ncdb) was performed to identify patterns of care and determine the survival impact of adjuvant hysterectomy.
A radical hysterectomy is a procedure used to treat cervical cancer that involves removing the uterus, cervix, tissue around the cervix and the upper part of the vagina. A simple hysterectomy removes the uterus (both the body of the uterus and the cervix) but not the structures next to the uterus (parametria and uterosacral ligaments). The pelvic lymph nodes are usually removed as part of this operation.
This is called a recurrence. It aims to remove all the cervical cancer. Robotic radical hysterectomy (rrh) offers an alternate minimally invasive.
A hysterectomy is typically only a treatment for early stage cervical cancer. Who is a candidate for a simple hysterectomy? If the cancer is at a very early stage, such as stage ia, most doctors believe it is safe to continue the pregnancy to term and have treatment several weeks after birth.
These cells can go on to grow and spread into a new problem. Hysterectomy (simple or radical) trachelectomy; Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer in women worldwide.
1,2,3 for more than a century, radical hysterectomy was performed predominantly through an open abdominal approach. Recurrence probably depends somewhat on how advanced the cancer was, and it. Cervical cancer starts out as abnormal cellular changes in the cervix, the part of the uterus that opens to the vagina.
Was diagnosed with stage 1b2 cervical cancer and booked in for a radical hysterectomy on the 10th june, all went well kept my ovaries went home on the 13th june. Skip forward 3 days i was in excruciating pain and had to be rushed back to hospital for an emergency. Cervical cancer hysterectomy 25 jun 2020 19:44.
A radical hysterectomy is the removal of the womb, cervix, tissue around the cervix (parametrium) and upper part of the vagina. Schockaert et al 5 recommended that cervical and vaginal colposcopy should be performed prior to hysterectomy due to cin. Surgery for invasive cervical cancer.
You have a history of cervical cancer or moderate to severe cervical changes—continue to have screening for 20 years after your surgery. However in developing countries, where there is limited access to radiotherapy, locally advanced cervical cancer may be treated with a combination of chemotherapy and hysterectomy (surgery to remove the womb and the neck of the womb, with or without the surrounding tissues). If your cervix or fallopian tubes were not removed, your risk of developing cancer in these organs is low.
Procedures to treat invasive cervical cancer are: It is the only gynecological cancer that can be prevented through regular screening. Often these patients are younger, between ages 20 and 40.
You have no history of cervical cancer or cervical changes—you do not need screening.