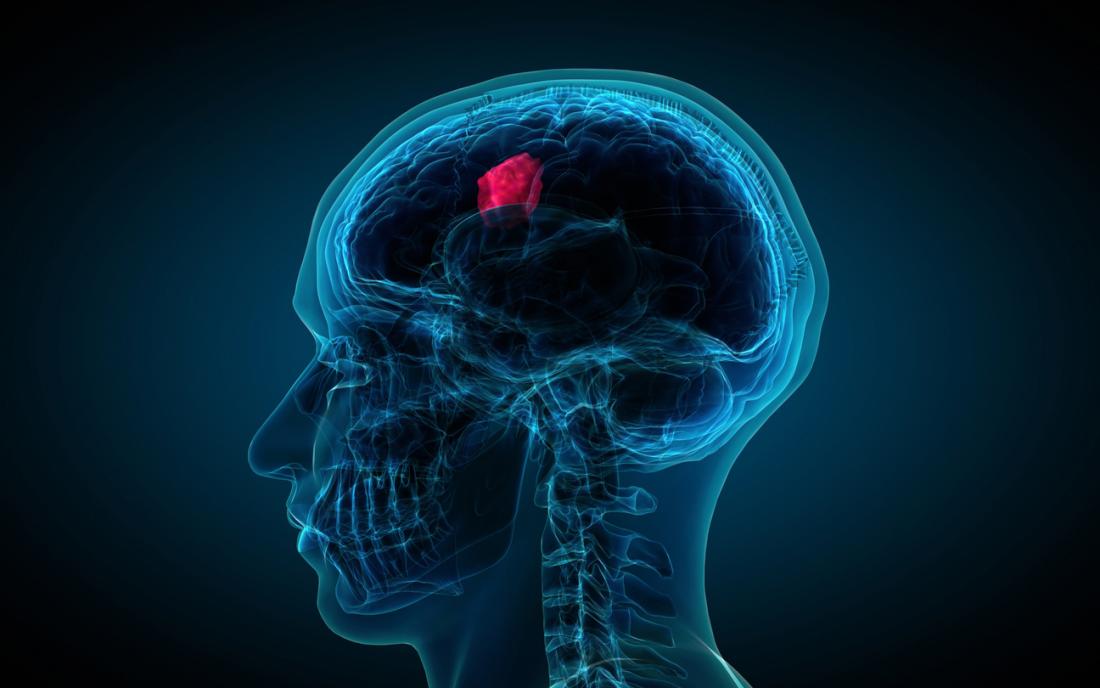
Typically benign brain tumors meningioma. This can be caused by growth of the tumor itself, swelling in the brain, or blockage of the flow.
They originate in one part of the body and move, or metastasize, reaching the brain.
Brain tumor and cancer. Definition • brain cancer is a disease of the brain in which cancer cells (malignant) arise in the brain tissue. A general symptom is caused by the pressure of the tumor on the brain or spinal cord. Your brain is locked into place by the skull.
Metastatic tumors to the brain affect nearly one in four patients with cancer, or an estimated 150,000 people a year. Cancer research uk has more on types of brain tumours. The speed at which a brain tumor grows, or regrows, can vary greatly, and it’s important to work with your treatment team to monitor any changes and catch a.
Brain tumor survival rate depends primarily on the type of cancer that a patient has been diagnosed with. Types of brain tumors • benign: Tumors that start in the brain are called primary brain tumors.
Many others are diagnosed with a secondary brain tumour. Secondary brain tumors are malignant because benign tumors don’t spread to other organs. Brain tumors can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
Metastatic tumors are considered cancer and are malignant. Changes in this gene increase the risk of developing brain tumors (particularly gliomas), as well as some other cancers. There are more than 40 major types of brain tumours, which are grouped into two main types:
Specific symptoms are caused when a specific part of the brain is not working well because of the tumor. Most benign tumors grow slowly and do not spread to other parts of the body. A recent study stated that brain and other nervous system cancers is the 10th leading cause of.
Signs and symptoms of brain or spinal cord tumors may develop gradually and become worse over time, or they can happen suddenly, such as with a seizure. If cancer spreads to the brain from another part of the body, it is called a brain metastasis, metastatic cancer, or a secondary brain tumor. Brain tumors lisa m deangelis the new england journal of medicine, 2011.
Cancer cells grow to form a mass of cancer tissue (tumour) that interferes with brain functions such as muscle control, sensation, memory, and other normal body functions. Not all brain tumors are cancerous, and benign tumors can result in similar. Brain and spinal cord tumours can affect children and adults.
Cancers that have spread to the brain from somewhere else in the body are called secondary brain tumours or brain metastases. They originate in one part of the body and move, or metastasize, reaching the brain. Brain tumours (primary) and brain metastases in adults national institute for health and care excellence (nice), july 2018.
For many people with a brain tumor, they were diagnosed when they went to the doctor after experiencing a problem, such as a. Tumours that start in the brain are called primary brain tumours. Many brain tumors are cancerous.
Ependymomas and oligodendrogliomas also are types of brain tumors that may be malignant. As a benign brain tumor grows, it will cause symptoms. Tumors in any part of the brain might increase the pressure inside the skull (known as intracranial pressure).
Brain metastases have traditionally been treated with surgery or radiation therapy. Grade 3 and 4 brain tumours are cancerous (malignant) tumours that grow more quickly and are more difficult to treat. How a brain tumor is different than brain cancer.
If the tumor breaks through the covering on the brain and starts to spread, then it is considered to be malignant. Brain tumours are also called primary (which start in the brain) and secondary (which spread to the brain). This can be caused by growth of the tumor itself, swelling in the brain, or blockage of the flow.
Brain tumors are growths of malignant cells in tissues of the brain. Brain cancer can have a wide variety of symptoms including seizures, sleepiness, confusion, and behavioral changes. Brain tumors occur when cells in your brain begin to grow out of control.
Using t cells to target malignant brain tumors. Principles and practice of oncology (10th edition) vt devita, ts lawrence, sa rosenberg lippincott, williams and wilkins, 2015. Meningioma is the most common primary brain tumor, accounting for more than 30% of all brain tumors.
Typically benign brain tumors meningioma. Tumors that spread to the brain are called metastatic brain tumors. Recurrence both benign brain tumors and malignant brain cancers are able to regrow, though patients with benign brain tumors are less likely to experience a recurrence.
The problem is that with both of these conditions, the. Gene changes acquired during a person�s lifetime it�s usually not known why people without inherited syndromes develop brain or spinal cord tumors. Brain tumours can affect people of any age, including children, although they tend to be more common in older adults.
German cancer research center (deutsches krebsforschungszentrum, dkfz) summary: Though brain cancer is a rare type of cancer, but in all cns (central nervous system) disorders, just brain tumors account for about 80% of the entire risk. More than 11,000 people are diagnosed with a primary brain tumour in the uk each year, of which about half are cancerous.
Tumours can start in any part of the brain or related structures. Brain cancers include primary brain tumours, which start in the brain and almost never spread to other parts of the body, and secondary tumours (or metastases), which are caused by cancers that began in another part of the body. Most of the brain tumors are secondary forms of tumors.
Metastatic brain tumors include tumors that arise elsewhere in the body (such as the breast or lungs) and migrate to the brain, usually through the bloodstream. Symptoms of a brain tumor can be general or specific. Lung cancer, skin cancer, breast cancer, and kidney cancer can metastasize to the brain.
Meningiomas originate in the meninges, the outer three layers of tissue that cover and protect the brain just under the skull. Start here to find information on brain cancer treatment, research, and statistics. Some types of brain cancer, such as meningioma, ependymoma and oligodendroglioma, are highly treatable, while others may be less responsive to curative therapies.
But not all brain tumors are cancerous. For example, more than half of all gliomas diagnosed in adults are glioblastomas, a very aggressive form of brain cancer. A brain tumor is a growth of new cells on any part of the brain.